* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy – Where does it come from and why does it produce waste?
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
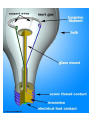
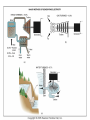
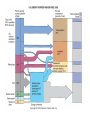
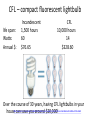
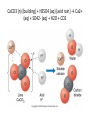
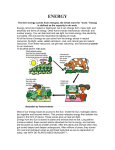
With your closest table mates: Write the answer to your assigned question. Remember to show work! HOMEWORK CHECK Resources & Reserves Resources ≠ Reserves • Resources – amounts of material that are known/ assumed to exist that can be extracted NOW or in the FUTURE for a POSSIBLE profit $ • Reserves – known amounts of material that can PRESENTLY be extracted for a PROFIT – “proven” Changing estimates • Why do reserves of resources usually last much longer than most early estimates predict? • How does technology influence the estimates of reserves and resources? Resource Depletion static, exponential, real world Energy – Where does it come from? ES 302 Objectives • What is energy? • What forms does it come in & how do we use it? • Understand that ALL sources of energy have costs and benefits What is Energy? • Energy “The ability to do work”. • Remember: The amount of energy in the universe is constant. What are the 2 major laws??? - Laws of thermodynamics What are the 6 major forms? - light, chemical, nuclear, mechanical, electrical, heat Make a circuit • Circuit = energy circle What is electricity? • The movement of electrons • As electrons move through metal wires, they rub against the wire – creating friction. This resistance creates heat and even light! • But where does this supply of electrons come from? What is a watt? • 1 watt = energy to lift 100 g (or 1 Newton) in 1.0 seconds. • It is a measure of energy over time Other Units of Energy • 1 calorie • 1 Btu (British thermal unit) • 1 Q (quad) = 1 quadrillion Btu (very large!) – The U.S. uses ~ 1 quad of energy about every 3.7 days • 1 kWh = one kilowatt of electricity over 1 hour How is electricity made? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AbUjieML FSo • Can you list the steps? • Check it out! Magnets & Generators • • • • • • Energy sources, for example coal, are burned which boils water, which produces steam The steam spins a turbine The turbine spins a magnet The magnet creates a flow of electrons This flow of electrons travels from the power plant to your home! How can changing a light bulb reduce greenhouse gases? 1st Law of Thermodynamics • “Conservation of Energy Law” – Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. • Energy in the universe is constant. • If you can’t destroy energy, you CAN change its form! – EX: Matches – EX: Light Bulb 2nd Law of Thermodynamics • “Energy Quality Law” – When energy changes form, some useful energy is always degraded to lower quality, less useful energy. • Low temperature heat is the least useful energy form! • EX: 90% of energy in gas (chemical) is changed to heat! • Only 5-10% of the electricity flowing through a light bulb is converted to light energy (the rest is heat). Energy Quality Energy in = Energy Out But the quality is always lower It takes energy to get energy • Before it’s useful… Oil must be 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Found Pumped Transported Refined Transported burned Net energy • Total useful energy available from the resource over its lifetime minus the amount of energy used and wasted • Example: – 10 units of energy in oil in ground – Use 8 units to find, extract, process, transport – 2 units of net energy available Energy Quality • The measure of the energy’s ability to be used to produce mechanical or electrical energy • Low temperature heat has the LOWEST quality – You can’t cook with it, you can’t move anything with it, you can’t even heat with it – Power plants are designed to release it into space Did you beat Mrs. Loch? • You analyzed your (presumed) usage of electricity – That energy is secondary • Primary Energy Resources: The fossil fuels(oil, gas, and coal), nuclear energy, falling water, geothermal, and solar energy. • Secondary Energy Resources: Those sources which are derived from primary resources such as electricity, fuels from coal, (synthetic natural gas and synthetic gasoline), as well as alcohol fuels. How can changing a light bulb reduce greenhouse gases? CFL – compact fluorescent lightbulb life span: Watts: Annual $: Incandescent 1,500 hours 60 $76.65 CFL 10,000 hours 14 $328.60 Over the course of 30 years, having CFL lightbulbs in your househttp://www.mnn.com/earth-matters/translating-uncle-sam/stories/cfl-vs-incandescent-battle-of-the-bulb can save you around $20,000! Two sides to everything. Byproducts of electrical generation • Burning coal Air: Mercury, CO2, SO2, NO2, fly ash Water: thermal pollution, acid rain Ground: bottom ash Example of the Laws of Conservation of Matter and Thermodynamics Global Warming Acid Rain Smog Burning Coal = CO2 + SO + H20 + Ash + (CxHxSxOx) Light + Noise + Heat CaCO3 (n) [building] + H2SO4 (aq) [acid rain] → Ca2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) + H2O + CO2 Acids and Bases Water molecules can react to form individual ions: H2O H+ + OH• In pure water this occurs naturally but the amount of H+ is always = to the amount of OH- so water remains neutral ACID:Any compound that forms H+ ions in solution BASE: Any cmpnd that forms 0H- ions in solution Example of the Laws of Conservation of Matter and Thermodynamics Global Warming Acid Rain Smog Burning Coal = CO2 + SO + H20 + Ash + (CxHxSxOx) Light + Noise + Heat Cartoon: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V1O34cqerqs Mini-FBL lesson What processes involve the transfer of carbon? Carbon Cycle Drawing • Make your own, UNIQUE, drawing of the carbon cycle. Include the following: – Photosynthesis, decomposition, respiration, combustion (LABEL ALL) – Include yourself somewhere in the cycle – Point out where humans interfere/alter the carbon cycle What is our best immediate energy option? 1. Cut out unnecessary energy waste by improving energy efficiency 2. Transition to a renewable or solar age – Sun, wind, flowing water, biomass, geothermal, hydrogen gas 3. Burn more coal & synthetic gas/liquids 4. Natural gas 5. Nuclear power Other Units of Energy • 1 calorie = amount of heat needed to heat 1 g of water 1 degree Celsius – 1 cal = 4.187 Joules • 1 Btu (British thermal unit) = amount of heat energy needed to raise the temp of 1 pound of water by 1 degree Farenheit – 1 Btu = 1,054 joules; 252 calories • 1 Q (quad) = 1 quadrillion Btu (very large!) – The U.S. uses ~ 1 quad of energy about every 3.7 days • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xPjESsHwg&feature=related – Very slow explanation of current & voltage. Nice analogy to water (river, lake) • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k7Sz8oT8 ou0 – Cardboard generator constrxn (7:44)