* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Activity: A Pyroelectric Smart Sensor
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Geophysical MASINT wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
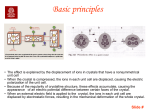
Activity: A Pyroelectric Smart Sensor PVDF-A polymer with many uses What is a Smart Sensor? We will use the term “Smart Sensor” to refer to systems that employs a sensor device mated to microelectronics. In this activity we will use metal coated PVDF films as our sensor system and a computer will take the place of the microelectronics. The system used in this activity is not engineered to minimize size and power consumption but clearly those would be goals in any widely deployed commercial device. Preparation for Activity Items Needed: PVDF sensor films; electronic components for circuits A and C (to be described) ; computer with data acquisition hardware/software. Am understanding of Piezoelectric Effect An understanding of Pyroelectric Effect An understanding of the role of molecular structure in determining the piezoelectric properties of PVDF Discussion Points Why is the b form of PVDF piezoelectric? How is the b form of PVDF Produced? What is the relationship between piezoelectric effect and the pyroelectric effect? What does the infrared spectrum of PVDF tell us about the wavelengths where the pyroelectric properties of PVDF might be most easily observed? Representations of the molecular structure of the vinylidene difluoride (VD) monomer and of the a and b forms of the PVDF polymer. F H F H VD-wire PVDF-b form PVDF-a form VD-space filling Infrared Spectrum of PVDF taken on a Bruker IFS 66v spectrometer, equipped with a DTGS detector and a KBr beamsplitter. Note that the strong absorption around 1000 cm-1 Discussion Points II How can we detect the piezoelectric or pyroelectric effect exhibited by a PVDF film? What is needed in terms of electronic and computer components to produce a smart sensor? Commercially available metal coated piezoelectric PVDF sensor elements A Film in (mm) B Electrode in (mm) C Film in (mm) D Electrode in (mm) t (µm) Cap (nF) .520 (13) .400 (10) .980 (25) .580 (14.70) 205 .500 .640 (16) .484 (12) 1.63 (41) 1.19 (30.17) 205 1.38 Electronic Circuits PVDF generates a measureable voltage Circuits with a very high Input impedance required Low power consumption, battery operated systems desirable for portability. (A) Impedance Adaptor, Voltage Follower (B) Electric Charge Measurement (C) Differential Amplifier, for measuring relative/combined signals Four Panel Thermal DetectionIndividual panels are connected to a dedicated circuit (A). USB data port interfaced to laptop computer gives system properties of a “smart sensor”. Voltage output 4 panel Pyroelectric Sensor when exposed to an asymmetrically located heat source Discussion Points Design a pyroelectic smart sensor system capable of to locating a single person in a room. Design a system which would make a PVDF pyroelectric sensor sensitive to a wide range of wavelengths. What information might be obtained from the voltage rise and decay exhibited on the thermal response curves What can be done to stabilize a PVDF pyroelectric sensor system?