* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP B Circuit Analysis
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
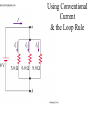
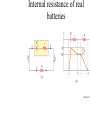
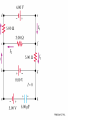
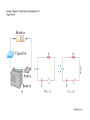
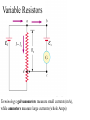
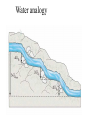
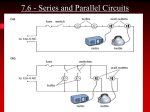
AP B Circuit Analysis Unlike the Regents, the AP B exam and college textbooks; 1) define current as the flow of + charge 2) have mixed circuits that with series and parallel elements 3) can have capacitors 4) can have more than one battery 5) the batteries aren’t necessarily ideal; they can have internal resistance that reduces voltage output 6) you may need to use a loop rule to figure out voltage drops Multiple batteries Using Conventional Current & the Loop Rule Internal resistance of real batteries Voltage Drops: When doing a loop analysis, V =0. Some V are +, some -. Throgh batteries, going from – to + is an increase, or + V. going from + to - is logically a loss of potential or -V. Through resistors: Going with the current is like going downhill, negative V, Going against current is like going uphill, +V. Variable Resistors Terminology: galvanometers measure small currents (mA), while ammeters measure large currents (whole Amps) Water analogy Sign Conventions while doing loop analysis Christmas lights A shunt is a low resistance parallel wire which will draw current When dialing different ranges on a meter you are connecting to shunts different resistances