* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
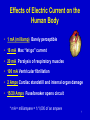
1 Electrical Safety 2 Electricity - The Dangers • About 5 workers are electrocuted every week • Causes 12% of young worker workplace deaths • Takes very little electricity to cause harm 3 Electrical Terms • Current -- electrical movement (measured in amps) • Circuit -- complete path of the current. Includes electricity source, a conductor, and the output device or load (such as a lamp, tool, or heater) • Resistance -- restriction to electrical flow • Conductors – substances, like metals, with little resistance to electricity that allow electricity to flow • Grounding – a conductive connection to the earth which acts as a protective measure • Insulators -- substances with high resistance to electricity like glass, porcelain, plastic, and dry wood that prevent electricity from getting to unwanted areas 4 Electrical Injuries There are four main types of electrical injuries: • Direct: Electrocution or death due to electrical shock Electrical shock Burns • Indirect - Falls 5 Electrical Shock Received when current passes through the body Severity of the shock depends on: 1. Path 2. Amount of current 3. Length of time • LOW VOLTAGE DOES NOT MEAN LOW HAZARD 6 Effects of Electric Current on the Human Body • 1 mA (milliamp) Barely perceptible • 16 mA Max “let go” current • 20 mA Paralysis of respiratory muscles • 100 mA Ventricular fibrillation • 2 Amps Cardiac standstill and internal organ damage • 15/20 Amps Fuse/breaker opens circuit * mA = milliampere = 1/1,000 of an ampere 7 Dangers of Electrical Shock Currents more than 75 mA can cause a rapid, ineffective heartbeat -- death will occur in a few minutes unless a defibrillator is used Defibrillator in use 75 mA is not much current – a small power drill uses 30 times as much 8 9 Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter • This device protects you from dangerous shock • The GFCI detects a difference in current between the positive and neutral wires (This could happen when electrical equipment is not working correctly, causing current “leakage” – known as a ground fault.) • If a ground fault is detected, the GFCI can shut off electricity flow in as little as 1/40 of a second, protecting you from a dangerous shock 10 Burns • Most common shock-related injury • Typically occurs on hands • Very serious injury that needs immediate attention 11 Falls • Electric shock can also cause indirect injuries • Workers in elevated locations who experience a shock may fall, resulting in serious injury or death 12 Electrical Hazards and How to Control Them Why? 13 Electrical accidents are caused by a combination of three factors: 1. Unsafe equipment and/or installation, 2. Workplaces made unsafe by the environment, and 3. Unsafe work practices 14 15 16 Grounding Grounding creates a lowresistance path from a tool to the earth to disperse unwanted current. 17 Tools -Preventing Electrical Hazards • Inspect tools before use • Use the right tool correctly • Use double insulated tools • Others? Double Insulated marking 18 Exposed Electrical Parts 19 Control – Isolate Electrical Parts • Use guards or barriers • Replace covers What about 50 volts or more? 20 Control – Close Openings • Junction boxes, pull boxes and fittings must have approved covers • Unused openings in cabinets, boxes and fittings must be closed (no missing knockouts) Photo shows violations of these two requirements 21 Overhead Power Lines Equipment that can contact power lines? What is the minimum distance? 22 23 Cords & Wires Cords can be damaged by: Aging Door or window edges Staples or fastenings Activity in the area Remove cords by pulling on the plugs, not the cords 24 Clues that Electrical Hazards Exist • Tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses • Warm tools, wires, cords, connections, or junction boxes • GFCI that shuts off a circuit • Worn or frayed insulation 25 Safety-Related Work Practices Avoid Wet Conditions! 26 No Bare Ground on Temp Circuits Romex No Ground No Strain Relief Temp Cord 27 GFCI Needed Exposed Elec. Conductor Splices 1910.303(c) 28 No Ground 1910.304(f)(4) 29 30 You Find the Standard 31 1910.305(g)(2)(iii) 32 Flex Cords Protected From Damage 1910.305(a)(2)(iii)(g) 33 Too Many Conductors Per Conduit 1910.305(b)(2) 34 Improper Use of Junction Box 1910.305(g)(1) Flex Cord Protection 1910.305(a)(2)(iii)(G) 35 Flex Cords-Continuous Length 1910.305(g)(2)(ii) 36 Exposed Elec. Conductor 1910.303(g)(2)(i) Strain Relief 1910.305(g)(2)(iii) 37 50v or more shall be guarded 1910.303(g)(2)(i) 38 Equip. Free From Recognized Hazards 1910.303(b)(1) Metal Shavings 39 40 Machine Guarding??? Exposed Elec. Parts 1910.303(g)(2)(i) 41 (g)(2)(No Strain Relief 1910.305(g)(2)(iii) 42 Exposed Thermostat 1910.303(g)(2)(i) 43 Summary Electrical equipment must be: Listed and labeled Free from hazards Used in the proper manner If you use electrical tools you must be: Protected from electrical shock Provided necessary safety equipment 44 The movement of electricity measured in amps is called A.Voltage B.Current C.Resistance 45 A conductive connection to the earth which acts as a protective measure is called. A. Resistance B. Current C.Grounding D.Insulator’’ 46 The most common electrical related injury is A. Falls B. Electrical burns C. Electrocution 47 How many amps can cause your heart to go into ventricular fibrillation. A. 75 mA B. 15 Amps C. 20 Amps 48 At what voltage is an electrical conductor required to be protected against contact? A. 50 volts B. 120 volts C. 30 volts 49 Credits • Some photos from safteng.net used with permission. • Disclaimer: Some of the photos or videos used in this presentation are from numerous sources, most of which are not identifiable. We do not claim any ownership of these videos. Not do we have any association with the owners. And only use them to illustrate the concepts of our safety programs. If copyright owners wish to have their pictures or videos removed from this presentation at any time please, just let us know. 50