* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power factor (Pf)
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
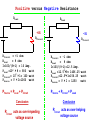
Technical Presentation on the new Power Saving Unit (PSU) Introduced By View Power Electrical Power Types Almost all bulk electric power is generated, transported and consumed in an alternating current (AC) network. Elements of AC systems produce and consume two kinds of Power: Real Power “P” (measured in watts) It accomplishes useful work (e.g., running motors) Reactive Power (measured in var). supports the voltages that must be controlled for system reliability To Simplify Things to all of us... You can’t move the wheelbarrow (active power delivery) unless you lift the arms! (reactive power) Power Factor Power factor (Pf) = The cosine of the angle between Voltage and current signals = cos φ. Power factor (Pf) = The cosine of the angle between useful power and Total power = cos φ = (P/S) Current Motor Current Magnetic current S=Total Power (KVA) Q Magnetic Power (KVAr) Useful current P=Useful Power (KW) Why improve Power Factor? The benefits that can be achieved by applying the suitable Power Factor correction are: Environmental benefit. Reduction of power consumption due to improved energy efficiency. Reduced power consumption means less greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel depletion by power stations Reduction of Electricity Bills Extra kVA available from the existing supply Reduction of I2R losses in transformers and distribution equipment Reduction of voltage drop in long cables Extended equipment life – Reduced electrical burden on cables and electrical components . Electricity Bill! Penalty Equation For a PF between 0.72----0.92, the penalty per year in L.E (Pen.) is calculated as follows: Pen. = KWHr per year × (0.92-average PF) × 0.5 For a PF below as follows: 0.72, L.E the penalty per year in L.E (Pen.) is calculated Pen. = KWHr per year × (0.92-average PF) × 1.0 L.E Numerical Example For 500000 KWHr with PF 0.8, we get For 500000 KWHr with PF 0.6, we get Pen=30000 L.E Pen=160000 L.E Electricity Bill! Bonus For a PF above 0.92, the Bonus per year in L.E is calculated as follows: Bonus = KWHr per year × (PF-0.92) × 0.5 L.E Numerical Example For 500000 KWHr with PF 0.96, we get Bonus=10000 L.E How to improve Power Factor? Power factor correction is achieved by the addition of capacitors in parallel with the connected motor or lighting circuits and can be applied at the equipment, distribution board or at the origin of the installation. So, what is happening? System with without Power Power factor factor correction correction Cosφ = (P/S) P (Watts) Cosθ = (P/S1)QC(VARS) φ θ QL-QC (VARS) S1(VA) QL(VARS) S (VA) Capacitors contained in most power factor correction equipment draw current that leads the voltage, thus producing a leading power factor. If capacitors are connected to a circuit that operates at a nominally lagging power factor, the extent that the circuit lags is reduced proportionately. Now; we can say that Power factor correction succeeded in the following: 1. Decreasing the shift between P and S, thus increasing PF 2. Decreasing the reactive power Q, thus reducing or eliminating the penalty from the electricity bill Power factor correction Failed in 1. Decreasing the active power “P” That yesterday What was about Today? B-Tech Leads a revolution and proudly introduces its new product Power Saving Unit PSU PSU PSU relies on a new technology that uses special capacitors, with unique specifications. PSU Capacitors are chemically treated, such that they gain a negative resistance PSU Non PSU Capacitors Used for PFC Q Positive Resistance S ≈880 More P consumption PFC P PSU Capacitors Negative Resistance Used for PFC Active Power Saving S Over-helping Q source PFC ? P Positive versus Negative Resistance RLoad RLoad +VE -VE RCircuit RCircuit RCircuit = +1 ohm RLoad = 9 ohm I=100/(9+1) = 10 Amp. PLoad =102 × 9 = 900 watt PCircuit= 102 × 1= 100 watt PSource = V × I=1000 watt RCircuit = -1 ohm RLoad = 9 ohm I=100/(9-1)=12.5 Amp. PLoad =12.52×9= 1406.25 watt PCircuit=12.52×1=156.25 watt PSource = V × I = 1250 watt PSource = PLoad + PCircuit PSource + PCircuit = PLoad Conclusion RCircuit acts as over-impeding voltage source Conclusion RCircuit acts as over-helping voltage source PSU Why PSU ? 1- When used with loads supplied from an electrical network, it can save up to 40% of the Active Power 2- When used with loads supplied from Diesel generators, it can effectively save the amount of used fuel 3- When used with inductive loads, it can safely improve the PF, thus eliminating any penalties and gain Bonus 4- It has much less dimensions compared with PFC units 5- It operates automatically to suit different load variations 6- It has much simple design, and needs much less maintenance PSU Why PSU ? 7- Our clients no longer need to increase their input power for further loadings, they can increase their loads up to 40 % without any changes in the feeders. 8- PSU is being Guaranteed by B-Tech for five complete years, through which professional maintenance and supervision is given 9- Has much competitive Price compared to the percentage saving, where the client mostly regain his investment in about one year 10- The usage of PSU simply reduces the end production marginal cost