* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Instruments for Radi..
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
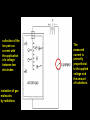
Instruments for Radiation Detection and Measurement Lab # 3 (1) • In nuclear medicine it is important to ascertain the – Presence – Type – Intensity – Energy of radiations emitted by radionuclides • Two commonly used devices – Gas-filled detectors – Scintillation detectors Gas-Filled Detectors • The operation of a gas-filled detector is based on the ionization of gas molecules by radiations, followed by collection of the ion pairs as current with the application of a voltage between two electrodes. • The measured current is primarily proportional to the applied voltage and the amount of radiations. collection of the ion pairs as current with the application of a voltage between two electrodes ionization of gas molecules by radiations The measured current is primarily proportional to the applied voltage and the amount of radiations. • The two most commonly used gas-filled detectors are •At higher voltages 1000 to 1200 V, – Ionizationfrom chambers counters used becomes forfrom measuring high the current •At• Cutie-Pie a lower voltages 50 to intensity radiation sources, such as output identical regardless 300from V, only the primary ion of x-ray machines how many ion pairs pairs formed by the initial • Dose calibrators measures the activityare of radiopharmaceuticals produced by the radiation are collected. incident radiation. – Geiger-Müller (GM) counters. Dose Calibrators • one of the most essential instruments for measuring the activity of radionuclides – Cylindrically shaped – Sealed chamber with a central well – Filled with argon and traces of halogen at high pressure Geiger-Müller (GM) Counters • One of the most sensitive detectors Scintillation Detecting Instruments • g-ray detecting equipment • Most commonly used: – well counters – Thyroid probes – g or scintillation • All these instruments are g-ray detecting devices • Consist of: • Collimator (excluding well counter) • Sodium iodide detector • Photomultiplier tube • Preamplifier • Pulse height analyzer • Display or Storage • Scintillation detectors consist of scintilator emitting flashes of light after absorbing gamma or x radiation. The light photons produced are then converted to an electrical pulse by means of a photomultiplier tube. The pulse is amplified by a linear amplifier, sorted by a pulse-height analyzer and then registred as a count. Different solid or liquid scintillators are used for different types of radiation. In nuclear medicine, sodium iodide solid crystals with a trace of thallium NaI(Tl) are used for gamma and x ray detection. The light photons will strike the photocathode of a g rays from a source interact in the sodium iodide photomultiplier The pulse is first amplified by a preamplifier and then by a linear amplifier detector and light photons are emitted. (PM) tube and a pulse is generated at the end of the PM tube.