* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of radiations transnational 6
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
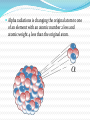
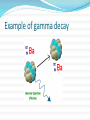
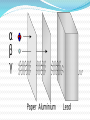
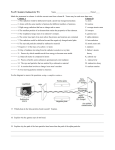
Alpha radiations Alpha radiations consist of: -two neutrons -two protons Alpha radiations is changing the original atom to one of an element with an atomic number 2 less and atomic weight 4 less than the original atom. Example of alpha decay Beta radiations Beta radiations take the form of: -electron -positron The positron has a particle with the size and mass of an electron, but with a positive charge, emitted from an atom. Example of beta decay Gamma radiations Gamma radiations do not consist of any particles. It is a photon of energy being emitted from an unstable nucleus. Example of gamma decay X-ray radiations X-ray radiations are very similar to the gamma radiations with the difference being that they come from the electron cloud. Neutron radiations Neutron radiations consist of a free neutron Differences between alpha, beta and gamma radiations Alpha radiations are the easiest to stop just with a thin layer of paper. Beta radiations can travel a few meters in the air due to the small mass. It can be stopped by a thick piece of wood or a stack of paper. Gamma waves can be stopped by a thick or dense enough layer material , with high atomic number materials such as lead or depleted uranium being the most effective form of shielding Stopped by Alpha radiation Beta radiation Gamma radiation Paper √ X X Wood √ √ X Plastic √ √ X Aluminium √ √ X Lead √ √ X Thick lead √ √ √ Depleted uranium √ √ √ Deflection in an magnetic/electric field Alpha radiation is attracted by the negative pole Beta radiation is attracted by the positive pole Gamma radiation is not attracted by any pole Sources https://www.mirion.com/introduction-to-radiation- safety/types-of-ionizing-radiation/ https://www.wikimedia.org http://hps.org/publicinformation/ate/faqs/radiationty pes.html A presentation by Razvan, Jannes, Angelica, Svetlozar This project has been funded with support from the European Commission. This publication [communication] reflects the views only of the author, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein.