* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Instantaneous Reclosing
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
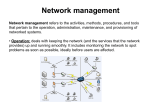
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Protective relay wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power Quality Impacts of Distributed Generation Roger C. Dugan Sr. Consultant Electrotek Concepts, Inc. Tennessee Tech. February 9, 2004 Introduction • Renewed interest in Grid-connected DG – Utility Perspective • T & D Capacity Relief • Hedge against high market prices – End User Perspective • CHP and Improved Reliability • Incentives from Utility – Commercial Power Producer • Sell kWh or “ancillary services” Electrotek Concepts, Inc 2 Emphasis of This Presentation • Units connected to distribution (MV) – Typically < 10 MW – Commonly 1-2 MW – Frequently owned by end user • Impact of these units on Power Quality – Operating conflicts – We will look at a few of the many … Electrotek Concepts, Inc 3 OverCurrent Protection Conflicts Typical Overcurrent Protection FEED ERS BREAKER R EC LOSER FUSED LATERALS Electrotek Concepts, Inc 5 Only One Device Has to Operate Operating Device FEED ERS Fault Current BREAKER R EC LOSER FUSED LATERALS Electrotek Concepts, Inc 6 Transmission Fault Protection Two Devices Must Operate to Clear Fault Electrotek Concepts, Inc Multiple Sources 7 LV Network Systems THESE DEVICES MUST OPERATE FAULT SUBSTATION PRIMARY FEEDERS TRANSMISSION SYSTEM FEEDER BREAKER OR RECLOSER LOW-VOLTAGE NETWORK NETWORK PROTECTOR Electrotek Concepts, Inc 8 Utility Fault Clearing • Due to cost, distribution systems are designed expecting only one source of fault current – Only one device has to operate • DG must disconnect to allow utility fault clearing process to continue • This is the source of most operating conflicts Electrotek Concepts, Inc 9 Reduction of Reach REDUCED REACH DUE TO DG INFEED X DG DG INFEED FAULT RESISTANCE REACH OF SUBSTATION BREAKER NORMAL REACH OF LINE RECLOSER Utility relays and DG relays may not know anything is wrong. Electrotek Concepts, Inc 10 Reduction of Reach • More of a problem at peak load – When peaking units are likely to be connected !! • More of a problem for high resistance faults • Longer fault detection times Electrotek Concepts, Inc 11 Instantaneous Reclosing Reclosing • Most faults are temporary • Reclosing is prevalent in North America • Reclosing Interval: 0.2 – 5 sec – “Instantaneous” < 30 cycles Electrotek Concepts, Inc 13 Reclosing, cont’d • If DG does not get off, two bad things could happen: – DG is damaged by the reclose • Shafts • Winding damage – Fault is not cleared • Reduced reliability • Damage to utility system Electrotek Concepts, Inc 14 Reclosing DG Must Disconnect Here Electrotek Concepts, Inc 15 Instantaneous Reclosing • Utilities use this for PQ concerns • Increases the probability that DG will not disconnect in time – Makes it almost a certainty that some won’t • If 1-2 sec, most operations will be easily detected by DG protection • Some utilities use 5 sec reclose on feeders with DG Electrotek Concepts, Inc 16 Unintended Consequences ... Voltage Drop After Fault VOLTAGE PROFILE BEFORE FAULT VOLTAGE PROFILE AFTER RECLOSE Electrotek Concepts, Inc 18 Low Voltage After Interruption • A problem when there is a fault at peak loading – When peaking DG is likely to be on !! • This is often the most limiting condition for how much DG can be accommodated without change – Particularly on rural feeders – 500 – 1000 kW Electrotek Concepts, Inc 19 Ferroresonance Sometimes Conflicting Interconnect Requirements Collide … Ferroresonance DG Required to have separate Transformer and disconnect at first sign of trouble G 1) Fuse blows or switch opens 3) Ferroresonance develops Electrotek Concepts, Inc 2) DG breaker detects negative sequence and trips leaving transformer isolated on cable capacitance with no load/generation 21 Ferroresonance Electrotek Concepts, Inc 22 Ferroresonance Waveform 4 Voltage, pu 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 0.000 0.050 0.100 0.150 0.200 Time, sec Electrotek Concepts, Inc 23 Reduced Insulation Arrester Duty for SLG ARRESTERS SUBJECTED TO LINETO-LINE VOLTAGES G UTILITY INTERRUPTING DEVICE OPEN PERMANENT LINETO-GROUND FAULT Electrotek Concepts, Inc UNGROUNDED TRANSFORMER CONNECTION 25 Varying Generation Varying Generation Example 10 000 ft 115 kV 12.47 kV 10 000 ft 1000 kW 20 000 ft Regulator 500 kW 600 kvar 336 MCM ACSR (Untransposed) Unbalanced impedances Wind Gen 8 MW Rapidly-varying “load” Electrotek Concepts, Inc 27 Varying Generation Wind Farm Voltage 8000 7900 7800 V, volts 7700 Regulator Operations 7600 7500 7400 7300 7200 7100 7000 1 301 601 901 1201 t, seconds Electrotek Concepts, Inc 1501 1801 2101 2401 28 Transformer Connection and Ground Faults Grd Wye-Delta Connection • Some claim this is the best way to interconnect DG – Same way as nearly all central station generation is connected – However, most utilities don’t allow this connection on their system. Electrotek Concepts, Inc 30 Wye-Delta Connection FAULT M AIN FAULT CONTRIBUTION FROM EPS 1 (MULTI-GROUNDED NEUTRAL) CONTRIBUTION FROM DR TRANSFORM ER G Electrotek Concepts, Inc 31 Problems with Wye-Delta • • • • Increases ground fault current Interferes with coordination Faulted Circuit Indicators get fooled Transformer subject to failure – Special design and/or neutral reactor – Utilities often discourage “Specials” Electrotek Concepts, Inc 32 On Wye-Wye • Most common U.S. connection • Generally well behaved • Does not block Triplen Harmonics – Leads to “Harmonic Surprise” when many machines paralleled with utility system • Also occurs with Delta-Wye – 2/3 pitch machines lessens the impact Electrotek Concepts, Inc 33 Conclusions • Interconnected DG likely to increase • DG must adapt to Distribution protection system • Too much infrastructure already in place to overhaul the system to better accommodate DG • Who would pay for it? Non-participating ratepayers? Electrotek Concepts, Inc 34 Conclusions • DG impact on Power Quality – Often good for individual end users • Largest gainers: Those with high-value product that suffer sustained interruptions • But, should not expect power quality improvement in all areas – Maybe slightly negative for utility • Contributes to operating conflicts • Can we see it in the Average indices? Electrotek Concepts, Inc 35 Conclusions, cont’d • Revisit Overcurrent Protection – Utilities may have to change some practices – Instantaneous reclosing ? – Use of line fuses • Tradeoffs for Transformer Connections – WYE-Delta good for DG but not for ground fault coordination • Special engineering req’d for some DG application. Electrotek Concepts, Inc 36 Despite These Conflicts … • DG can almost always be successfully engineered – Larger conflict may be over who pays – Some long-standing utility practices may have to be changed Electrotek Concepts, Inc 37 How Much DG ? • What is the “No Changes” “Penetration Limit” ? – Typical: 15% of feeder capacity – 5% - 10% if Rural Electrotek Concepts, Inc 38