* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CMOS Schmitt Trigger Test Circuit
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
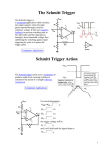
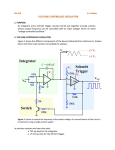
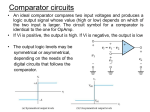
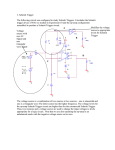
CMOS Schmitt Trigger Test Circuit Mitchell Belser, P.E. Visiting Instructor Department of Computer Engineering Jackson State University [email protected] What is a Schmitt Trigger • A type of comparator. • A comparator is an electronic circuit whose output state changes when its input reaches a certain value. • A comparator’s output state will change at the same input value whether the input voltage is increasing or decreasing. • A noisy signal can cause the output to change state randomly. Schmitt Trigger Operation • The Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit that has two threshold voltages. • When the input is higher than the upper threshold, the output is high. • When the input is lower than the lower threshold, the output is low. Schmitt Trigger Operation • The Schmitt trigger employs positive feedback. • When the input is between the two thresholds the output state does not change. • The difference between the two thresholds is the hysteresis. Schmitt Trigger Transfer Curve Schmitt Trigger History • The Schmitt trigger was first invented by Otto H. Schmitt in the 1934. • Vacuum Tube based design. • A Thermionic Trigger, Journal of Scientific Instruments, 15 January 1938 pg 24-26 Schmitt Trigger v-minus v-plus R10 R7 R9 output 2 R8 3 V1 1 2 input 3 V2 1 R6 Thermionic Trigger Schmitt Trigger Implementations • Comparator with positive feedback • Bipolar transistor Schmitt trigger • CMOS transistor Schmitt trigger Comparator with Positive Feedback R11 U1 R12 output Vin Comparator with Positive Feedback Bipolar Schmitt Trigger vdd Upper switching point voltage: R2 R3 output Vth = R4/(R4+R3)*Vdd Q2 R1 Lower switching point voltage: Vtl = R4/(R4+R2)*Vdd Q1 input R4 R5 BJT Schmitt Trigger CMOS Schmitt Trigger VDD Upper switching point voltage: M5 β1/ β3 = W1L3 / W3L1 M6 M4 Lower switching point voltage: β5/ β6 = W5L6 / W6L5 GND U1A input M2 VDD M3 M1 GND U3A U4A output Applications • Input buffers for digital signals. • Crystal oscillator circuits. • Clean up noisy signals (switch debounce). • Speed up signals with slow edges. Problem Description and Motivation for Improvement The conventional method for characterizing a CMOS Schmitt trigger is to ramp up the input voltage until the output state changes. The input voltage that results in the output changing state is the high threshold voltage VTH. In a similar manner, the low threshold voltage VTL is determined by reducing the input voltage until a state change occurs at the output. This method is widely used. The major draw back is the time that is required to search for the input voltage that results in a state change at the output. The proposed method would eliminate the need to perform a ramp search and thus greatly reduce the time needed to determine the switching threshold voltage levels. Specific Improvements Innovation : A CMOS Schmitt trigger circuit containing additional test circuitry that allows trigger voltage levels to be detected at the input without needing to ramp the input voltage. Important components of innovation: The test circuitry consists of combinational logic and a CMOS switch. Digital input signals determine whether the high or low threshold voltage is measurable. Traditional Schmitt Trigger Circuit VDD M5 M6 M4 GND U1A input M2 VDD M3 M1 GND U3A U4A output Schmitt Trigger Showing Effect of Test Circuitry VDD ►Test circuitry is shown in blue. ►Asserting test mode and vih input results in sout being shorted to the input. The gates of the feedback transistors are driven to vdd. The input is regulated to the high input threshold voltage VTH. ►Asserting test mode and vil input results in sout being shorted to the input. The gates of the feedback transistors are driven to gnd. The input is regulated to the low threshold voltage VTL. ►In normal operating mode the test circuitry has no effect on Schmitt trigger operation. M5 M6 M4 GND sout sout U6A 7402N U7A U4A 7402N M2 U8A VDD 7432N M3 M1 U2A 7408J VTL Test_en U5A input VTH 7408J M7 GND sout M8 U1A output Advantages of This Method Typical method requires input to be driven and output voltage to be monitored in order to determine the switching threshold voltage levels. Test circuitry allow thresholds to be measured at the input without driving input or monitoring the output. Simply setting a digital input causes the threshold voltage to be present on the input pin of the Schmitt trigger. . Simplifies test program and reduces test time resulting in increased profit margin. Measurement Data Part VDD C VCL-A4-5 VTH 5V 3.3 V A VCL-A4-3 STATIC 5V 3.3 V 4.21 2.63 4.22 2.64 RAMP VTL 2.92 1.69 2.98 1.73 VTH Frequency VTL 4.2 3.08 1 4.24 3.04 1k 2.64 1.84 1 2.64 1.76 1k 4.24 3.12 1 4.28 3.06 1k 2.66 1.80 1 2.64 1.72 1k Measurement Waveforms VDD= 3.3V Ramp frequency = 1kHz Summary • Schmitt trigger threshold test circuit. • Measure rising and falling threshold levels. • Ramping input and monitoring output state is no longer necessary. • Reduction in test time. • Increase in profit due to reduction in test time.