* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Voltage-Controlled Oscillator
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Light switch wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
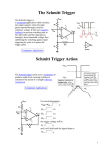
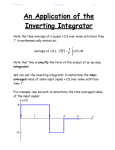
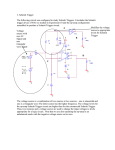
PH-315 A. La Rosa VOLTAGE-CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR 1. PURPOSE: An integrator and a Schmitt Trigger circuitry will be put together to build a device whose output frequency can be controlled with an input voltage; hence its name “voltage-controlled oscillator.” 2. VOLTAGE-CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR Figure 1 shows the different components of the device (obtained from reference 1), broken down into three main sections to facilitate its analysis. Vmonitor 2/3 V+ 1/3 V+ Integrator C = 0.05 F Schmitt Trigger V+ V+ 100k Vin 50k + 100k V+ 3160 + Vout 50k 100k 50k 100k Switch 100k Figure 1. Device to control the frequency of the output voltage. An unusual feature of the circuit is its operation using a single positive supply.1 In previous sessions we have also used: a 741 op amp for the integrator a LF 411 op amp for the Schmitt trigger. = 0.05 F 0.01F capacitor (depending on the frequency range you want to work) V+ - + V+ 50k Switch 10k 50k Switch MOS FET Fig.2 Optional switches suggested in Ref 1. TASKS: i) Analyze the Schmitt Trigger first. Make a diagram of the expected hysteresis curve behavior. Vout Vmonitor ii) Analyze how the Schmitt Trigger control the switch section (the transistor). iii) For the two cases (switch off and switch on) analyze the behavior of the integrator. iii-1) Obtain an expression for Vmonitor as a function of time when the switch is OFF. Hint: It will help to sketch the flow of current (magnitude and direction) across the resistors and capacitor. iii-2) Obtain an expression for Vmonitor as a function of time when the switch is ON. iii-3) Obtain an expression that can allow evaluating how long doest it take for the Schmidt trigger to change its output back and forth. iv) Based on the above analysis, estimate the time-period at which the output voltage changes states. Highlight the variables that influence the value of the period. According to this analysis, adjust the proper values of the different component in order to have a clear measurable variation of the period as the DC input voltage varies. Hence, measure how much the frequency of the output voltage changes as a function of Vin (for various values of C.) In addition to C, feel free to change the values of other components. v) Plot frequency of Vout vs Vin. Describe the agreement between the expected theoretical values and the experimental results. vi) Use the oscilloscope to monitor simultaneously both the output voltage from the integrator (Vmonitor) and Vout . 1 Horowitz and Hills, “The Art of Electronics,” 2nd Edition, Cambridge University Press.