* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrokinetics
Lift (force) wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Flow measurement wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli's principle wikipedia , lookup
Compressible flow wikipedia , lookup
Reynolds number wikipedia , lookup
Flow conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Aerodynamics wikipedia , lookup
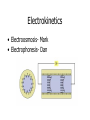
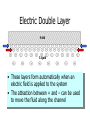
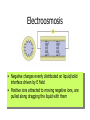
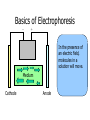
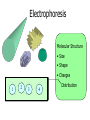
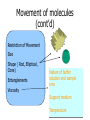
By Dan Janiak and Mark Hanna September 15 2003 Electrokinetics • Electroosmosis- Mark • Electrophoresis- Dan Electric Double Layer Solid Liquid • These layers form automatically when an electric field is applied to the system • The attraction between + and – can be used to move the fluid along the channel Electroosmosis • Negative charges evenly distributed on liquid/solid interface driven by E field • Positive ions attracted to moving negative ions, are pulled along dragging the liquid with them Electroosmotic Flow Profile • Relatively uniform flow profile compared to pressure driven flow Flow Profiles Compared • Pressure driven flow is not uniform due to indirect driving force • Electroosmotic driven flow is more uniform due to a direct driving force on each atom Electroosmosis + and + • Generated naturally when a potential field is applied • Flow can be controlled with voltage adjustments • Flat, symmetrical flow profile • Sensitive to solution and surface chemistry • Requires homogenous fluid and constant surface conditions • Flow needs to be monitored so it is possible to account for these changes Basics of Electrophoresis - + In the presence of an electric field, molecules in a solution will move. Medium Cathode Anode Factors influencing electrophoresis Promoting Factors Retarding Factors Potentially either Voltage Physical resistance pH Current Viscosity Buffer ions High surface charge Interactions Buffer additives Low mass Low surface charge Buffer concentration Molecular dissociation High mass Molecular association Non-spherical shape Electrophoresis, the Basics D.M. Hawcroft Electrophoresis Molecular Structure • Size • Shape • Charges + + + + 1 + + + + + + + + + + - 2 - + + - - + + - - 3 + - + + + + - - - - - 4 - - - - - Distribution Properties of the medium and buffer solution Medium Paper Cellulose acetate Gels Sample molecules must be solvated, ionized. Concentration and pH play a large role in electrophoresis. Movement of molecules E*Q E = Strength of applied electric field Q = Molecular charge Molecules with greater charge densities move faster and farther than ones with smaller charge densities Molecules move toward electrodes of opposite polarity =V/E Movement of molecules (cont’d) Restriction of Movement Size Shape ( Rod, Elliptical, Cone) Entanglements Viscosity Nature of buffer solution and sample ions Support medium Temperature Summary Electrokinetics Electroosmosis (Surface Interaction) Electrophoresis (Separation) Processes occur simultaneously