* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Power System SMJE 2103
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
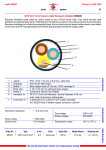
Electrical Power System SMJE 2103 Electrical Power Delivery System Power Flow / Load Flow • A numerical analysis for future planning of operational power system in order to optimize generated power. • The objective is to produce following inform: i- voltage magnitude and phase angle at each bus ii- real and reactive power flowing in each element iii- reactive power loading on each generator Power Delivery “Overhead Lines - Components” Power Delivery “Transmission Line – Single Line” Power Delivery “Towers - types” Power Delivery “Towers - size” Height of tower is determine by- H h1 h2 h3 h4 h1=Minimum permissible ground clearance h2=Maximum sag h3=Vertical spacing between conductors h4=Vertical clearance between earthwire and top conductor Power Delivery “Conductor - types” ACSR Conductor(Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced) AAC(All Aluminium Conductor) AAAC(All Alloy Aluminium Conductor) Power Delivery “Line – equivalent circuit” L’ = Inductance R’ = Resistance C’ = Capacitance G’ = Leakage Resistance Power Delivery “Conductor - resistance” - Short line (up to 80 km) - Medium-length lines (up to 240 km) - Long line (above 240 km) Power Delivery “Transmission Line” Power Delivery “Power Cable” Power Delivery “Power Cable” Power Delivery “Power Cable - losses” Power Delivery “Power Cable - losses” Dielectric used for cable insulation must have following properties: • • • • • • High insulation resistance High dielectric strength Good mechanical strength Immune to attack by acids and alkali in the range 0-100o C Should not be too costly Should no be hygroscopic (tending to absorb water), or if hygroscopic should be enclosed in a water tight covering Power Delivery “Cable - resistance” Power Delivery “Cable - inductance” Power Delivery “3- Core Cable - inductance” Power Delivery “3- Core Cable – inductance (M & C)” Power Delivery “3- Core Cable – inductance” (Measured) Power Delivery “3- Core Cable - inductance” (Measured) Example/Tutorial • A 3 core, 3 phase metal sheathed cable on testing for the capacitance gave the following results: i) Capacitance between all conductors bunched and sheath, Cm1=0.6uF ii) Capacitance between two conductor bunched with sheath and third conductor, Cm2=0.36 uF With the sheath insulated find, a) Capacitance between any two conductors b) Capacitance to neutral c) Charging current if cable is connected to 11kV, 3 phase, 50 Hz system Power Delivery “3- Core Cable – Gas-pressure” Power Delivery “3- Core Cable – Gas-pressure” Power Delivery “3- Core Cable – Gas-pressure” Power Delivery “Insulator” Power Delivery “Insulator - Types” There are several types of insulators but the most commonly used are : 1)Pin Insulator 2)Suspension Insulator 3)Strain Insulator and 4)Shackle insulator. Power Delivery “Pin Insulator” - Nonconducting material such as porcelain, glass, plastic, polymer, or wood. - Upto 33 kV Power Delivery “Pin Insulator” Power Delivery “Suspension Insulator” - For high voltages (>33 kV) - Each unit or disc is designed for low voltage, say 11 kV - The number of discs in series would obviously depend upon the working voltage Power Delivery “Suspension Insulator” Power Delivery “Strain Insulator” - Dead end of the line or corner or sharp curve. - For low voltage lines (< 11 kV). - Two or more strings are used in parallel. Power Delivery “Strain Insulator” Power Delivery “Shackle Insulator” - Used for low voltage distribution lines. - Horizontal or vertical position. Power Delivery “Shackle Insulator” Power Delivery “Insulator” Power Delivery “Circuit Breaker” Power Delivery “Circuit Breaker” Power Delivery “Circuit Breaker” Power Delivery “Circuit Breaker” Power Delivery “Circuit Breaker” Power Delivery “Switchgear (GIS)” Power Delivery “Switchgear (GIS)” Power Delivery “Switchgear (GIS)” Power Delivery “Switchgear (GIS)”