* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 51: Electrical Technology - News
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
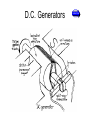
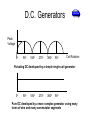
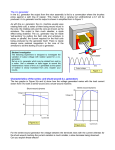
Unit 51: Electrical Technology The Characteristics and Principles of AC and DC Generators and the features of a Range of difference Power Station Course Aims • NDGTA At the end of this course the learner will be able to… 1. Know the methods used to produce electrical energy 2. Know the properties and applications of conductors, insulators and magnetic materials 3. Know the physical arrangements of supply, transmission and distribution equipment 4. Know how electrical energy is used to support applications of electrical technology Agenda NDGTA • At the end of the session the learner will be able to… – Describe DC Generators D.C. Generation • NDGTA DC Generator - Molecular Expressions Florida State University D.C. Generators NDGTA D.C. Generators NDGTA • A rotating armature coil passes through a magnetic field that develops between the north and south polarities of permanent magnets or electromagnets. • As the coil rotates, electromagnetic induction causes a current to be induced into the coil. • The current produced is an alternating current. • However it is possible to convert the alternating current into a form of direct current (DC) D.C. Generators NDGTA • This AC to DC conversion is accomplished though the use of a split-ring commutator. • The purpose of the split-ring commutator is to reverse the armature-coil connection to the external load circuit at the same time that the current induced in the armature coil reverses. • This causes DC of the correct polarity to be applied to the load at all times D.C. Generators NDGTA Peak Voltage 0o 90o 180o 270o 360o 90o Coil Rotation Pulsating DC developed by a simple single-coil generator 0o 90o 180o 270o 360o 90o Pure DC developed by a more complex generator using many turns of wire and many commutator segments Factors affecting the voltage developed NDGTA • The voltage developed by a DC generator depends upon… – The strength of the magnetic field – The number of coils in the armature – The speed of rotation of the armature • The voltage can be increased by increasing any of these factors The Voltage Developed by a DC Generator NDGTA • Vo = (Z x n x Ф) / 60 • Where Vo is the voltage developed across the generator brushes in volts • Z = the total number of armature conductors • N = speed of rotation in r.p.m. • Ф = magnetic flux per pole in webers • Given: A 4-pole DC generator rotates at 1200 r.p.m. The armature has 36-slots and each coil has 4-turns of wire. The magnetic flux per pole is 0.05 webers. Find the voltage output of the DC generator? The Voltage Developed by a DC Generator • Note each turn of the wire has two conductors, thus… • Z = 2 x 36 x 4 = 288 • Thus Vo = (288 x 1200 x 0.05) / 60 • Vo = 288 volts NDGTA