* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multi-functional Packaged Antennas for Next
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Direction finding wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Beams wikipedia , lookup
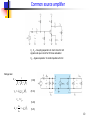
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Signal Corps (United States Army) wikipedia , lookup
Bellini–Tosi direction finder wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
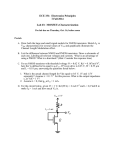
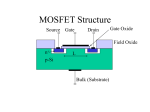
The sinusoid signal will be distorted if the ac input signal is large. However, the distortion can be neglected if the signal is small. 1 2 Graphical solutions 3 Fig. 5.18 4 5 Small signal equivalent circuits Assuming operation in the saturation region Where For small signal case is negligible gm = transconductance Where, The gate current for FET is negligible Small signal equivalent circuit 6 Dependence of gm on Q-point and device parameters We know that and VGSQ Vto IDQ K But from (5.3) Therefore μn- surface mobility of electron Cox- capacitance of gate per unit area 7 More complex equivalent circuits • At higher frequencies small capacitance have to be added between device terminals • Also in the saturation region iD versus VDS is considered to be constant. This is not actually the case. The drain current, iD increases slightly as VDS increases. In order to take care of that we must add a drain resistance rd in the small signal model. 8 Example Determine the values of gm and rd the MOSFET characteristics shown below. From equation 5.34, we have, obtain iD = 6.7 mA at VDS = 4 V and iD = 8 mA at VDS = 14 V. Thus, the reciprocal of rd is calculated as: 8 6.7 mA 0.13 103 S 1 i D 14 4V rd vDS Thus, rd = 7.7 KΩ 9 Common source amplifier C1, C2 – Coupling capacitors short circuit for AC signals and open circuit for DC bias calculation CS – bypass capacitor small impedance for AC Voltage Gain RL' 1 1 1 1 rd Rd RL v0 ( g mvgs ) RL' vin v gs Av v0 g m RL' vin (5.38) (5.39) (5.40) (5.41) 10