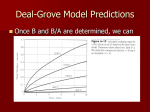
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
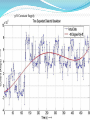
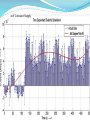
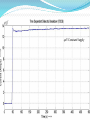
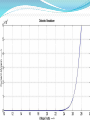
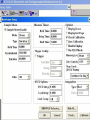
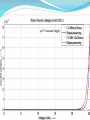
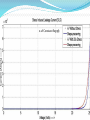
CV Characterization Using 4284A LCR Meter & 4155C Semiconductor Parametric Analyzer Device Characterization Lab Center of Excellence in Nanoelectronics Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Metallization Oxide Reliability Device Testing (Capacitance and Vth) New Process, Device(FET’s) and Circuit Developments C-V/I-V Measurements High Frequency Low Frequency (Qusistatic C-V) Sequential C-V measurements Simultaneous C-V and I-V measurements Quality Testing Reliability Testing: Breakdown Measurement -Breakdown Voltage & TDDB -Charge to Breakdown (QBD) Current-Voltage Measurement -Oxide Leakage Current -Stress Induced Leakage Current(SILC) DUT: n-type Semiconductor 32nm SiO 2 Area=1.34×10-7cm2 Breakdown Voltage Voltage or Current is Applied until Oxide breaks down -constant V or constant I method -Ramped V or Ramped I method Simple Indication of Oxide Quality Time Dependent Dielectric Breakdown (TDDB) Large number of samples of measured parameter (I or V) taken while another parameter is constant (V or I) Used to study the reliability of the Dielectric and to predict the life time Since a particular source (I or V) is applied for a longer period of time, the effect of I or V stress can be studied. (Temperature stress is also possible) 30V Constant Supply 20V Constant Supply 40V Constant Supply Charge to Breakdown (QBD) Constant or stepped current is forced through dielectric The charge starts to increase and it breaks down the oxide total applied charge can be integrated to calculate the definite amount of charge need to break down the oxide Oxide leakage current In operating range leaky oxide exhibits linear dependency on applied voltage Characteristic curve depends on the thickness of the oxide because the tunneling phenomena is different for different oxide thickness Stress Induced Leakage Current(SILC) I-V characteristics measured after each stress cycle IVStressIVStressIVStress…. Stress can be voltage or current stress over time Damage due to stress increases the current in subsequent IV measurements. 40V Constant Supply 0.1A Constant Supply