* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reverse Breakdown Voltage Studies
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
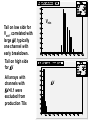
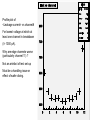
Reverse Breakdown Voltage Studies • Use Minglee’s leakage current as a function of reverse bias voltage measurements to look for evidence of ESD at array level. • Post-hoc analysis of arrays with dead TX and reverse leakage data available gives no hints. • Statistical analysis of full data set from Minglee – excludes files with strange leakage behaviour, one or more channels with leakage current> 1 nA for V<10V). – This leakage is not an artefact of the test system but is not correlated with ESD. – These devices were excluded from production to be safe. 1 Leakage vs Reverse Bias Voltage Define breakdown when leakage current > 1000 pA Determine bias voltage at which (a) >=1 channel in breakdown: Vmin (b) All 12 channels in breakdown: Vmax Plot Vmin and Difference DV= Vmax - Vmin 2 Vmin Tail on low side for Vmin, correlated with large DV, typically one channel with early breakdown. Tail on high side for DV All arrays with channels with DV>0.1 were excluded from production TXs DV 3 Taiwan QA • Removed all TXs with strange data ie high leakage (>1 nA for low voltage). • Removed all obvious suspicious TX with DV>= 0.1 V. • Allowed through 5 intermediate cases with 0.06 < DV < 0.1 • None of these 5 have died. 4 Profile plot of <Leakage current> vs channel# For lowest voltage at which at least one channel in breakdown (I> 1000 pA). Why are edge channels worse (particularly channel 11) ? Not an artefact of test set-up Must be a handling issue or effect of wafer dicing. 5