* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download photodiode
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Shockley–Queisser limit wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
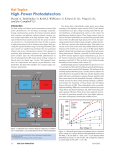
CUÑADO, Jeaneth T. GEQUINTO, Leah Jane P. MANGARING, Meleria S. cgmarts@ee12 PHOTODIODE A photodiode is a type of photodetector capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation. The common, traditional solar cell used to generate electric solar power is a large area photodiode. OPERATION • A photodiode is designed to operate in reverse bias. • Photoelectric effect. • Photocurrent. HISTORY & THEORY • Photodiode technology developments came out of the basic developments of the PN junction diode that started in the 1940s in earnest. Applications for the use of the PN junction diode were found outside the basic use of rectifying signals. • Photodiode technology was refined in the 1950s and in the latter part of that decade the PIN photodiode was developed. Light absorption in the wide depletion area of the PIN structure was first investigated in a paper published in 1959 by Gartner. Although silicon has been the favoured material for photodiodes, germanium can also be used, and its use was first demonstrated in 1962 MATERIALS STRUCTURE TYPES + Advantages for the Photodiode detector are high NIR sensitivity and high speed. - Disadvantages are limited amount of pixels and no UV response. 1. PIN photodiode 2. PN photodiode 3. Avalanche photodiode 4. Schottky photodiode ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES CHARACTERISTICS Photodiodes are similar to regular semiconductor diodes except that they may be either exposed (to detect vacuum UV or X-rays) or packaged with a window or optical fiber connection to allow light to reach the sensitive part of the device. Many diodes designed for use specifically as a photodiode use a PIN junction rather than a p-n junction, to increase the speed of response. CHARACTERISTICS SIGNIFICANCE • In most cases, the photodiode is used to deliver a trigger signal to an electrical device when it is either exposed to a UV ray or X-ray. It may also be used to deliver the same trigger signal when the light source is either turned off or the photodiode is blocked from the light source. • A function that a photodiode can perform is to keep an electrical device operating through the process of converting light into a power signal or voltage. • Photovoltaic mode and photoconductive mode are naturally occurring reactions to the light APPLICATIONS • P-N photodiodes are used in similar applications to other photodetectors, such as photoconductors, charge-coupled devices, and photomultiplier tubes. They may be used to generate an output which is dependent upon the illumination (analog; for measurement and the like), or to change the state of circuitry (digital; either for control and switching, or digital signal processing).. • Photodiodes are used in consumer electronics devices such as compact disc players, smoke detectors, and the APPLICATIONS many applications either photodiodes or photoconductors may be used. Either type of photosensor may be used for light measurement, as in camera light meters, or to respond to light levels, as in switching on street lighting after dark • Photosensors of all types may be used to respond to incident light, or to a source of light which is part of the same circuit or system. A photodiode is often combined into a single component with an emitter of light, usually a light-emitting diode (LED), either to detect the presence of a mechanical obstruction to the beam (slotted optical switch), or to couple two digital or analog circuits while maintaining extremely high electrical isolation between them, often for safety (optocoupler). APPLICATIONS • Photodiodes are often used for accurate measurement of light intensity in science and industry. They generally have a more linear response than photoconductors. • They are also widely used in various medical applications, such as detectors for computed tomography (coupled with scintillators), instruments to analyze samples (immunoassay), and pulse oximeters. • PIN diodes are much faster and more sensitive than p-n junction diodes, and hence are often used for optical communications and in lighting APPLICATIONS • P-N photodiodes are not used to measure extremely low light intensities. Instead, if high sensitivity is needed, avalanche photodiodes, intensified charge-coupled devices or photomultiplier tubes are used for applications such as astronomy, spectroscopy, night vision equipment and laser rangefinding. (According to temperature…) Photodiodes are basically reverse biased diodes with optical windows that allow like to shine on the PN junction. Like any diode, the leakage current (otherwise known as a photodiodes 'dark' current) increases exponentially with temperature in accordance to William Shockley's idea diode equation. This is known as the quantum efficiency of the photodiode. If the quantum efficiency of a photodiode will increase with temperature, so as well as the thermally induced noise. EFFECTS Archi ves BreakDown Voltage: For small active area devices, by definition breakdown voltage is defined as the voltage at which the dark current becomes 10 A. Since dark current increases with temperature, therefore, breakdown voltage decreases similarly with increase in temperature. The End cgm@ee12 All Rights Reserve 2012 melerz.pictures