* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.3 Sex Cell Development, Birth review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
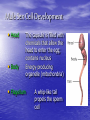
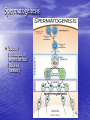
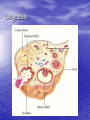
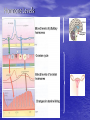
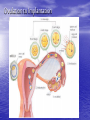
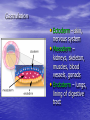
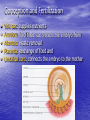
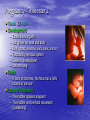
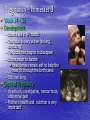
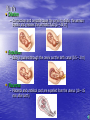
Sex Cell Development & Human Conception Male Sex Cell Development • Head • Body The capsule is filled with chemicals that allow the head to enter the egg; contains nucleus Energy-producing organelle (mitochondria) • Flagellum A whip-like tail propels the sperm cell Spermatogenesis • Sperm produced in seminiferous tubules (testes) Egg Production • The eggs form and mature in two ovaries, which contain • • follicles Each follicle contains an egg When the egg is ready, the ovary wall ruptures and the egg is released into the oviduct – This is called ovulation • After ovulation, the ruptured follicle forms into the corpus luteum Note: • The ovary does not produce new egg cells throughout adult life • The ovary contains approximately 40 000 immature follicles at puberty, and that number continually decreases • Only one follicle matures every month; the others break down and are absorbed by the ovary Oogenesis ♀ Hormones • FSH: Follicle stimulating hormone – Signals the ovaries to produce mature eggs • LH: Luteinising hormone – Released by the pituitary gland (base of brain) • Progesterone – Released by corpus luteum • Estrogen – Reproductive hormone – Causes appearance of ♀ secondary sexual characteristics Hormones & Menstruation • • • • • • • • • • • Pituitary gland releases FSH FSH stimulates follicle development Developing follicle secretes estrogen ↑ estrogen levels stimulates thickening of endometrium Estrogen travels to pituitary, stimulating release of LH LH causes developing follicle to release a mature egg LH stimulates empty follicle to develop in corpus luteum Corpus luteum produces progesterone and estrogen ↓ progesterone increases thickening of endometrium Progesterone causes pituitary to decrease FSH production ↓ FSH and LH prevent more eggs from being released until progesterone decreases again Hormone Levels Fertilization • The head of the sperm breaks • • • • through the cell membrane of the egg Only one sperm enters the egg The egg (n) and sperm (n) nuclei combine together (2n) This is called a zygote The flagellum of the sperm is pinched off Ovulation to Implantation • The zygote undergoes many cell divisions • When it reaches the uterus, it has become a blastocyst (hollow ball of cells) – Outer cells of the blastocyst will become the placenta – Inner cells will form the embryo • Implantation occurs when the blastocyst attaches to the endometrium – This produces a hormonal signal that prevents the corpus luteum from disintegrating – If the corpus luteum breaks down, menstruation occurs Ovulation to Implantation Gastrulation • Ectoderm – skin, nervous system • Mesoderm – kidneys, skeleton, muscles, blood vessels, gonads • Endoderm – lungs, lining of digestive tract Conception and Fertilization • • • • • Yolk sac: supplies nutrients Amniom: fluid-filled sac protects the embryo from Allantois: waste removal Placenta: exchange of food and Umbilical cord: connects the embryo to the mother Pregnancy - Trimester 1 • Week 1 – 12 • 4 Weeks – Basic heart, large brain, limb buds, eyes, spine – Embryos have a tail • 8 Weeks – – – – – Cartilage replaced by bone The embryo is now a fetus Facial features, limbs, hands, feet, fingers, and toes are visible The nervous system responds to stimulus The internal organs begin to function • High Risks – Spontaneous abortions or miscarriages, birth defects • Signs of Pregnancy – Nausea/vomitting, frequent urination, no menstruation Pregnancy - Trimester 2 • Week 12 – 24 • Development – – – – – – External sex organs Hair grows on head and body Blink, grasp, swallow, suck, hear, and cry Functioning nervous system Skeleton development 300 mm long • Risks – If born at this time, the fetus has a 50% chance of survival • Signs of Pregnancy – The mother appears pregnant – The mother will feel fetal movement (quickening) Pregnancy - Trimester 3 • Week 24 – 38 • Development – Open eyes in 8th month – The fetus is very active (kicking, stretching) – The body hair begins to disappear – Bones begin to harden • Head bones remain soft to help the head fit through the birth canal – 500 mm long • Signs of Pregnancy – Heartburn, constipation, hemorrhoids, abdominal pain – Mother’s health and nutrition is very important Risks during Pregnancy Birth • Dilation – Contractions and oxytocin cause the cervix to dilate; the amnion breaks and releases the amniotic fluid (2 – 20 hr) • Expulsion – Baby is pushed through the cervix out the birth canal (0.5 – 2 hr) • Placental – Placenta and umbilical cord are expelled from the uterus (10 – 15 min after birth)