* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Paolo Macchiarini wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal development wikipedia , lookup
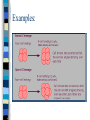
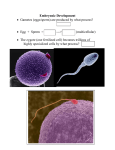
Development and Growth Embryology So…meiosis gives us gametes which unite through fertilization to form a fertilized zygote. Now what? 9 months later…. A baby is born with a complete body structure, both inside and out. How do we get there? We must look at the early stages of embryology (study of dev. embryos) as these early stages set up the body for the rest of the pregnancy Definitions Development- a series of events that give rise to a full grown organism Embryo- a multicellular organism in the early stages of development Differentiation- a series of changes that transforms unspecialized embryonic cells into specialized cells, tissues, and organs. Cleavage- series the zygote of cell divisions by After fertilization…. Zygote begins a series of cell divisions called cleavage Cleavage occurs every 20 hours. To produce more cells that decrease in size until all cells are the size they will be of the adult. Examples: 3 Stages Stage 1: Morula: Solid ball of cells Cells grow more numerous while their size decreases Stage 2: Blastula: Cell division keeps going and the cells begin to form a hollow fluid filled ball Embryo Development Stage 3: Embryo Development Gastrula- cells on one side of the blastula move inward and form a two layered embryo opening is createdblastopore Embryo Development The 2nd week of human development Gastrulation – early in development, a gut is created through an intucking of cells from the exterior of the embryo into the interior – It results in 3 basic germ layers • Ectoderm • Mesoderm • Endoderm Embryo Development The endoderm differentiates into – digestive tract – lungs – bladder The mesoderm differentiates into – skeleton – skeletal muscle – connective tissue Embryo Development The ectoderm differentiates into – skin – hair – brain – spinal cord Embryo Development By the 4th week of human development –Neurulation (nervous system) is underway –Gastrulation is complete Embryo Development By the 5th week of human development –Limb buds are present –Organs start to form Fetal Development By the 10th week of human development –Intestines are located in the abdomen –Fingernail development Fetal Development By the 15th week of human development –Fetus is very recognizable –While internal organs continue to grow and mature, the external appearance is very human-like Fetal Development By the 38th week of human development –Baby has reached full term and is ready to exit the uterus for the real world