* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animalia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
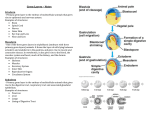
KINGDOM ANIMALIA CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTIC MULTICELLULAR HETEROTROPHIC (by ingestion) MOVE AT SOME POINT IN LIFE DIGEST FOOD TO GET NUTRIENTS LACK CELL WALLS SEXUAL REPRODUCTION TRENDS IN ANIMAL EVOLUTION CELL SPECIALIZATION CEPHALIZATION EARLY DEVELOPMENT BODY SYMMETRY BODY CAVITY FORMATION CELL SPECIALIZATION CELLS FORM TISSUES – EPITHELIAL (skin, lining of cavities) – CONNECTIVE (bone, blood) – MUSCULAR (heart, biceps) – NERVOUS (brain, nerves) CEPHALIZATION CONCENTRATION OF SENSE ORGANS AND NERVE CELLS AT FRONT END OF BODY EARLY DEVELOPMENT FERTILIZATION FORMS A ZYGOTE BLASTULA (hollow ball of cells) GASTRULA (stage when layers that produce adult tissues form) GERM LAYER FORMATION GERM LAYERS ECTODERM ENDODERM MESODERM GERM LAYERS – SEE PAGE 494 ECTODERM – Covers surface of embryo – Forms outer covering & CNS ENDODERM – Innermost germ layer – Forms lining of digestive tract, liver, lungs MESODERM – Located b/w ectoderm & endoderm – Forms muscles & most organs BODY SYMMETRY Animal’s body plans are adapted for how they get their food they may be motile (move) or sessile (don’t move) 3 TYPES OF BODY SYMMETRY Asymmetrical-no sponge) Radial-body symmetry (ex, Bilateral- body plan in which single line can divide body into 2 equal parts plan in which body parts repeat around center of body ANATOMICAL TERMS Dorsal- top or back Ventral- bottom Anterior- head end that goes first Posterior- tail end that follows Lateral- along the side (lengthwise) ANATOMICAL TERMS Dorsal Anterior Posterior Ventral BODY PLANS OR BODY CAVITY FORMATION ACOELOMATE- no body cavity b/w digestive tract and outer body wall ex. Platyhelminthes (flatworms) BODY PLANS OR BODY CAVITY FORMATION COELOMATE- body cavity forms and cushions organs, allows for growth of organs. Ex. Annelids (earthworm) FEEDING HETEROTROPHS HERBIVORES- as plants eat vegetation such FEEDING HETEROTROPHS CARNIVORES- eat other animals FEEDING HETEROTROPHS OMNIVORES- feed on both vegetation & other animals FEEDING HETEROTROPHS FILTER FEEDERS- feed by straining tiny floating plants FEEDING HETEROTROPHS DETRITUS FEEDERS- feed on tiny bits of decaying matter Sea Cucumber FEEDING HETEROTROPHS PARASITES- feed on living organisms usually destroying or injuring the host organism 2 MAIN GROUPINGS OF ANIMALS INVERTEBRATES – 95% of animal species – No backbone VERTEBRATES – 5% of animal species – Contains backbone ESSENTIAL FUNCTIONS OF ANIMALS FEEDING RESPIRATION CIRCULATION EXCRETION RESPONSE MOVEMENT REPRODUCTION VARIOUS ANIMAL FUNCTIONS HELP MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS OFTEN BY USING FEEDBACK MECHANISMS INCLUDING FEEDBACK INHIBITION EXAMPLE: DOGS GET HOT RUNNING, NERVOUS SYSTEM TRIGGERS PANTING. PANTING REDUCES BODY TEMPERATURE SO PANTING STOPS. 9 Major Phylum Board notes! Homework: page 508, #1-6, #8