* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
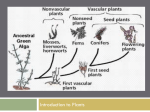
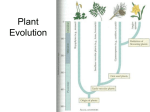
Chapter 13 Plants 13A Plants Botany- study of plants Most plants are autotrophic but NOT ALLsome heterotrophic, some parasitic Not all have chlorophyll! Not all are green! All are eukaryotic, all have tissues, some have organs All have cell walls of cellulose All sexually reproduce, many also asexual as well 12 Phyla grouped into 3 groups based on Vascular tissue (Y/N) and seeds (Y/N) Will learn 4 major groups 1. Non-vascular- Phylum Bryophyta- Moss (and 2 others) 2. Vascular seedless- Phylum PteridophytaFerns (& 3 others) 3. Vascular with seeds uncoveredGymnosperms- Phylum Coniferophyta- Pines (& 3 others) 4. Vascular with seeds coveredAngiosperms- flowering plants- Phylum Anthophyta- 2 classes: Monocots & Dicots Box on 333 Groups based on the # of seasons they grow in 1. Annuals- sprout, grow, produce flowers and seeds all in 1 growing season 2. Biennials- sprout and grow in 1 season but don’t produce flowers and seeds until the next growing season. Die after 2nd year 3. Perennials- grow year after year, mostly woody but some herbaceous with thick underground stems that live even when above ground stems and leaves die 13A-1 Phylum Bryophyta- Mosses No vascular (water conducting) tissues No seeds Very short <3cm Rhizoids anchor the moss (not true roots) Leafy shoot- leaf like, one cell layer thick Alternation of generations 2 stage life cycle Haploid gametophyte generation produces the diploid sporophyte generation which produces the gametophyte etc. In moss the dominant generation is the GAMETOPHYTE (leafy shoot) 1. Male and female leafy shoots Male= antheridium makes sperm Female = archegonium makes ovum 2. Water brings sperm to ovum fertilization 3. Zygote grows a stalk and capsule (sporophyte) which makes spores 4. Spores released 5. Spores grow into a protonema which then forms leafy shoots and rhizoids (gametophyte) Liverworts & Hornworts Also non vascular 2. Seedless vascular plants Main one is fern but also… Club Mosses and Horsetails 13A-2 Ferns: Phylum Pteridophyta Leaves called fronds, has vascular tissues but no woody stems, may be large Some are epiphytes (grow on other plants but not parasitic) Rhizomes – underground stems, produce fronds (young fronds called fiddleheads) Fronds produce spores = sori (collection of sporangia) Spores germinate heart-shaped prothallus (gametophyte) Archegonium & antheridium make ovum & sperm Ovum + Sperm Zygote (makes the sporophyte fronds) Sporophyte is the dominant generation Review of Ferns Leaves called fronds (many types of shapes) Rhizome Crosiers – underground stem or fiddle heads – young fronds Spores make heart shaped tiny plant that makes egg & sperm, needs water to fertilize, then grows the fiddle head, etc. 13A-3 Vascular with Seeds 2 Groups: Flowering & Nonflowering A. Gymnosperm = “Naked seed” not enclosed in fruit (ovary) Phylum Pollen Coniferophyta = cone-bearing = pines cones – near tip of branches Seed cones – female, contain ova Wind brings pollen to seed cones gametes unite, embryo develops mature seed released to form new tree