* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seed Reproduction
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
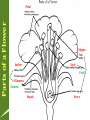
Seed Reproduction Chapter 9 Notes Seed Reproduction • Plants need to reproduce to carry on their species. • Plants reproduce due to the movement of pollen and seeds. Pollen • Pollen contains the males sperm. It is known as a gametophyte. When the pollen reaches female plant parts, fertilization occurs. • After fertilization, seeds form. These seeds are the plants offspring. Seeds – The seed contains an embryo, stored food (in the cotyledon), and a protective coat. Because the seed is so well protected and fed, the plant grown from it will grow faster compared to spores (seedless reproduction). Why would the seed want stored food and a protective coat? Two Types of Seed Reproducers • Angiosperms What’s the difference? • Gymnosperms Angiosperm • Angiosperms produce flowers which are used for sexual reproduction. Parts of a Flower Petal Stigma Anther Style Pistil Filament Stamen Sepals Ovary Angiosperm – The stamen is the male reproductive organ. – The pistil, the female reproductive organ, contains the ovary at its base. Angiosperm – The appearance of a plant’s flower can give clues about how the plant is pollinated. – After pollination and fertilization, a zygote forms and grows into the plant embryo. – Parts of the ovule develop into the seed coat and store food for the embryo. Angiosperm • Some seeds store food in cotyledons. • Other seeds store food in endosperm tissue Where are seeds found? • THE FRUIT. So…fruit is like the plant’s baby. Fact: Fruits have seeds. Vegetables do not. A true vegetable is usually a root. (potato, carrots, onion) Angiosperm Life Cycle A. Pollination happens when pollen grains from the anthers land on the sticky stigma of a pistil. B. The pollen tube grows from the pollen grain down through the style and into the ovary at the ovule. C. The sperm travels down and fertilizes the egg. The zygote develops. Gymnosperm • Gymnosperms develop seeds in cones. Gymnosperm – A pine tree or shrub is a sporophyte plant that produces male and female cones. – A female cone has two ovules which produce eggs. – Male cones produce and release pollen. Gymnosperm – When pollen blows into a female cone, fertilization and seed formation can occur. – Seed released by a female cone can take two or three years. Seed Dispersal • Seeds are dispersed by wind, gravity, animals, and water. Some seeds have trapped air which helps them float. – Germination occurs when the seed coat swells and breaks open. – Environmental conditions affect germination.