* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
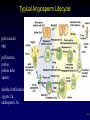
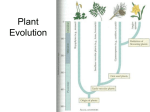
Overview of Plant Diversity Chapter 29 1 The Evolutionary Origins of Plants • Defining characteristic of plants is protection of their embryos. Land plants can be divided into two groups based on the presence or absence of vascular tissue. 2 The Evolutionary Origins of Plants • • • Adaptations to land – protected from desiccation - waxy cuticle gas exchange- stomata – evolution of leaves increased photosynthetic area Alternates Generations diploid generation alternates with haploid generation 3 • Plant Life Cycles diploid generation alternates with haploid generation – diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis Spores divide by mitosis, producing haploid gametophyte. – haploid gametophyte is the source of gametes – gametes fuse to form diploid zygote – 4 Mosses, Liverworts, and Hornworts • Bryophytes - avascular plants – sporophytes are attached to and nutritionally dependent on gametophytes – require water to reproduce sexually – most are small 5 Features of Vascular Plants • Vascular tissues – xylem – phloem – Earliest vascular plants lacked seeds Seedless Vascular Plants - Ferns 6 • Ferns are the most abundant group of seedless vascular plants. – greater development, independence, and dominance of fern’s Sporophyte Fern sporophytes have underground stem, the rhizome. sporangia in clusters, sori, on back of fronds Diploid spore mother cells in each sporangium undergo meiosis, producing haploid spores 7 • Seed Plants Seed Plants first appeared about 425 mya. – drought protection – enhanced dispersal – dormant phase increase embryo survival by waiting for favorable environmental conditions 8 • • Gymnosperms Seeds but lack flowers and fruits of angiosperms Four living groups – conifers – cycads – gnetophytes – Ginkgo 9 10 Angiosperms • • Ovules are enclosed within diploid tissues at time of pollination – carpel, modified leaf encapsulating seed, develops into fruit Monocots and eudicots – eudicots and monocots differ in: number of cotyledons leaf venation presence lateral meristems number of flower parts 11 12 Angiosperms • Structure of flowers 13 Typical Angiosperm Lifecycle polar nuclei egg pollination pollen pollen tube sperm double fertilization zygote 2n endosperm 3n 14