* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monocots Dicots
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
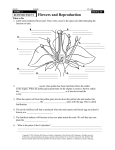
Plant Kingdom Plant Classification Plant Kingdom Bryophytes Tracheophytes Seedless Seeds Gymnosperms Angiosperms Monocots Dicots Bryophytes • • • • • Simplest plants Lack true stems and leaves Lack vascular systems Problem with fertilization Examples: Mosses, liverworts, hornworts Seedless Vascular Plants • Vascular tissue is present. • Moist environments. • Flagellated sperm rely on water. Snake Grass Monocots Dicots Stoma Cuticle-coated epidermal cell Light micrograph of a leaf’s stomata Stomatal Action Healthy stomata Closed Open Clogged stomata • Plant cells showing choroplasts inside. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What does the orange represent? How many sections does the orange have? What does this mean? What is the carrot? What type does it represent? Can you see rings in the carrot? What makes the rings? Briefly explain what the rings are. Where are the seeds of a strawberry? How many seeds do you think it has? Why would they be here? 8. Explain the difference between monocots and dicots. 9. Sketch both types, both flowers and stem cross section. 10. Look at two flower types under a scope. How many stamen are there? What are arrangements of stamen in relation to pistil (carpel)? 11. Sketch the underneath side of a leaf. What are the important structures. What is the purpose of these? Do they function the same in all plants? Name the differences. 12. Name two things you know now that you didn’t 1 hour ago. Division Common Name Dominant Fluid Generation Transport Sperm Transport Dispersal Unit Bryophyta Mosses Gametophyte Nonvascular Flagellated Sperm Spores Lycophyta Club mosses Sporophyte Vascular Flagellated Sperm Spores Horsetails Sporophyte Vascular Flagellated Sperm Spores Ferns Sporophyte Vascular Flagellated Sperm Spores Conifers Sporophyte Vascular Wind – Pollen Seeds Flower Plants Sporophyte Vascular Wind/Animal - Pollin Seeds Sphenophyta Pterophyta Coniferophya Anthophyta Vegetative Propagation • Bulbs – short stems underground, Onions • Runners – horizontal above ground stems, Strawberries • Tubers – underground stems, Potatoes • Grafting – cutting of a stem, attach it to closely related plant, Seedless oranges Plant Tropisms • Phototropism – response to sunlight, e.g. plants bend towards the light • Thigmotropism – response to touch, e.g. ivy grows around posts • Gravitropism – response to gravity, – Positive – roots – Negative – stems These responses are initiated by hormones, mostly of the class called Auxins Functions of Plant Hormones Gibberellins Promotes stem elongation Cytokinins Promotes cell division and differentiation Ethylene Induces leaf abscission and promotes fruit ripening Abscisic acid Inhibits leaf abscission and promotes bud and seed dormancy Flower Parts • Before fertilization can occur, the pollen grain on the stigma must germinate. • Each pollen grain contains a tube cell and a generative cell. • The tube cell forms a pollen tube that grows down inside the style to an ovule. The role of the pollen tube is to enter the stigma of the plant and to reach the ovule, allowing fertilization to take place. The tube cell does not increase in volume during the several centimeters growth of the pollen tube. It generally takes less than a day for the pollen tube to reach the ovule. • The generative cell divides to form two sperm that move down the pollen tube. • The pollen tube provides a pathway for the sperm to reach the egg cell in the ovule. • One sperm fertilizes the egg cell and together they form the zygote. • The other sperm unites with the polar bodies in the ovule and together they form the nutritive tissue for the zygote. Pollen Grains Grass Rose Root types Plant Biology Video