* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Flowering plants
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
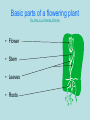
Flowering NCES 6L1.1 Kim Lachler updated 2015 Plants • Why are plants important to you? – Gives you oxygen – Gives you food The_Plant_Life_Cycle_and_Us.mov • Plants Are living (Biotic) They grow Reproduce Respond to their environment Flowering Plants • Make of 90% of all plants • They vary greatly in appearance and size. Fit in your hand Climb in Basic parts of a flowering plant The_Parts_of_a_Flowering_Plant.mov • Flower • Stem • Leaves • Roots The role of roots • Absorb water • Absorb nutrients • Provide an anchor • Store food Types of root systems • Tap root – Goes deep to find water. – Provides a strong anchor in the wind. • Fibrous – Fan out to find water – Roots are shallow. – the plant can easily be blown over in high winds. Root Close Up Root hair Root cap Stem supports the plant above the ground transports water and nutrients • Xylem - transports it up the plant • Phloem - flows it down the plant Leaves • Blade - makes up the broad part of the leaf. • Veins - transport nutrients and water. • Petiole - connects the stem and the leaf. Leaves are Busy • It is where the plants food is produced by a process called photosynthesis. light and carbon dioxide are taken in. oxygen is released. Flower • The flowers are responsible for reproduction. The Parts of a Flower • A bud is a developing flower • Sepal protect the bud The Parts of a Flower • Petals – usually colorful • Sepal – protected the bud sometime they fall off after the flower is formed The Parts of a Flower Pistil – female part Stigma – Sticky so the pollen will stick to it. Style – Tube like structure for support Ovary – Where the pollen goes down. It becomes the fruit Ovule – Where the seed develops The Parts of a Flower Stamen – male part Anther – Carries the pollen Filament – Supports the anther Two Types of Flowers • Perfect – has both male and female parts on the same flower. • Imperfect – have only the male or only the female parts on the same flower. Pollination 1)The petals attract birds and insects by their color or smell. 2)The bird or insect moves the pollen from the anther to the stigma. Spreading the Seeds • Birds and animals eat the fruit, which causes the seeds to be dispersed. • Wind can also disperse seeds. Protection • Plants have developed several different forms of protection: » Thorns » Poison Bibliography • The Great Plant Escape http://urbanext.illinois.edu/gpe/case1/c1m1a.html Accessed 5/17/10 • Happy Living Magazine http://www.happynews.com/living/gardening-flower/parts-floweringplant.htm Accessed 5/18/10 • Goggle Images http://www.google.com/images Accessed 5/17/10 • Discovery Education, http://streaming.discoveryeducation.com/ Accessed 6/09/10