* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roots, Stems, Leaves and Tissues 09
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
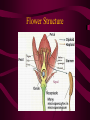
Roots, Stems, Leaves and Tissues Tissue Systems • Plants consist of four different types of tissues • Meristematic tissue is located at the tips of shoots and roots and is responsible for the growth that takes place in a plant’s lifetime • Meristematic tissue is the only tissue that produces new cells by mitosis and is found at the tips • Apical Meristems are a group of cells that reproduce at the tips of roots by mitosis, causing elongation of the root Tissues, cont. • Dermal Tissue- the outer covering of a plant is known as dermal tissue and usually consists of a single layer of epidermal cells • Vascular Tissue- tissue that carries food, water and minerals throughout the plant. – Made of many different types of cells – Allows transport of materials to defy gravity More Tissues • Ground tissue- the “meat” of the plant- the area between dermal and vascular tissue • Consists of three different types of cells Roots • Roots take in water and nutrients, anchor the plant in the ground and hold the plant upright • Taproots and fibrous roots are the two main types • Roots have a complex structure and allow the plant to transport materials easily Root Types taproot Fibrous root Stems • Stems produce leaves, branches and flowers • They hold the leaves up in the sunlight • They also allow for transport of materials between roots and leaves Leaves • The structure of leaves are optimized for absorption of sunlight • Photosynthesis- the bulk of leaves is made of a specialized ground tissue called mesophyll which is packed with chloroplasts • Transpiration- is the loss of water through the leaf • Gas exchange- carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged through the leaf’s surface Flowers • Flowers are the reproductive structure of flowering plants, also known as Anthophytes or Angiosperms • Flowers come in many shapes, colors and sizes, depending on the genetic make-up of the species • Flowers can turn into fruits once pollinated, which protect the seeds of the plant and aid in dispersal Flower Organs • Sepals protect the flower • Petals can be brightly colored and attract pollinators and provide them with a landing pattern • Stamens- Male reproductive part of the flowers, consists of the filament and the anther, produces pollen • Female reproductive part is the pistil, it consists of stigma, style and the ovary Flower Structure Sepal Pages to help 222, 644-646