* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bryophytes P.P.
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Indigenous horticulture wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Hydroponics wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
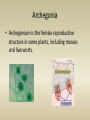
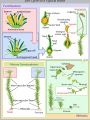
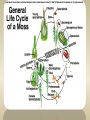
Bryophytes Bryophytes • Bryophytes are nonvascular plant; examples are mosses and their relatives. WHERE THEY ARE FOUND • THRIVE IN WET ENVIRONMENTS OR IN AREAS WHERE THERE IS LOTS OF RAINFALL AT LEAST PART OF THE YEAR – – – – – SWAMPS MARSHES NEAR STREAMS, RAINFORESTS ALONG THE WEST COAST OF BC & STATES Unique to Bryophytes • have no lignin usually • are small, low-lying, (generally) moistureloving plants • have no roots, only filamentous rhizoids THE ONLY LAND PLANTS WITH A DOMINANT GAMETOPHYTE! The sporophyte is parasitic on the gametophyte. This stems from the embryo being retained in the female sex organ of the gametophyte. Groups of bryophytes • Bryophytes included mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. Mosses Liverworts Hornworts LIVERWORTS • SCARCER THAN MOSSES • NEED TO LIVE IN PLACES THAT ARE CONSTANTLY WET • LOOK LIKE FLAT LEAVES GROWING ALONG THE GROUND HORNWORT • LOOK LIKE GAMETOPHYTE OF LIVERWORT • SPOROPHYTE LOOKS LIKE A HORN Mosses • The most common bryophytes are mosses, which are members of the phylum Bryophyta. • Mosses grow most abundantly in areas with water-in swamps and bogs, near streams, and in rain forests. BRYOPHYTES LACK SEVERAL CRITICAL ADAPTATIONS TO DRY PLACES • LACK WATER CONDUCTING TUBES – IN BRYOPHYTES, WATER PASSES FROM CELL TO CELL BY OSMOSIS & BY MEANS OF SURFACE TENSION AROUND THE STEMS – WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? WHAT ELSE? • BRYOPHYTES LACK PROTECTIVE SURFACE COVERING TO KEEP WATER FROM EVAPORTAING FROM THEIR CELLS • WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? THERE IS MORE • THEY LACK TRUE ROOTS – ROOTS CONTAIN WATER CONDUCTING TUBES THAT ENABLE A PLANT TO ABSORB AND TRANSPORT WATER EFFICIENTLY • THEY HAVE RHIZOIDS INSTEAD – WHAT IS THEIR FUNCTION? Rhizoids • Rhizoid are in fungi, a root like hypha that penetrates the surface of an object; in mosses, a long, thin cell that anchors the moss to the ground and absorbs water and minerals from the surrounding soil. Protonema • Protonema is the mass of tangled green filaments in mosses that forms during germination. Antheridia • Antheridum is the male reproductive structure in some algae and plants. Archegonia • Archegonium is the female reproductive structure in some plants, including mosses and liverworts. • During at least one stage of their life cycle, bryophytes produce sperm that must swim through water to reach eggs of other individuals. • Therefore, they must live in places where there is rainfall or dew for at least part of the year Role of Bryophytes • Many are pioneer plants, growing on bare rock and contributing to soil development. • In bogs and mountain forests they form a thick carpet, reducing erosion. • In forest ecosystems they act like a sponge retaining and slowly releasing water • They provide habitat for other plants and small animals as well as microorganisms like N2-fixing blue-green bacteria • Lacking a cuticle and transport tissue they readily absorb whatever is around them and can serve as bioindicators of pollution and environmental degradation