* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photosynthesis Pt 1 Light
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Photoacoustic effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Upconverting nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Laser pumping wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Transparency and translucency wikipedia , lookup
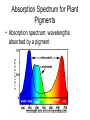
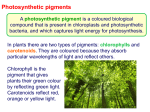
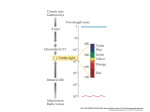
Photosynthesis Part 1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum • Light as a wave • Light travels in waves and its energy can be measured in wavelengths. • Short wavelengths are high energy • Long wavelengths are low energy Visible Light Spectrum • White light or visible light is a blend of all visible wavelengths • This range is from 400 to about 800nm • 1nanometer is 1 billionth of a meter! When Light Interacts with matter • 1. Light passes through the matter (transparent) • 2. Light is reflected (resulting in the colors you see) • 3. Light is absorbed (energy is released as heat or used to excite electrons to make chemical bonds!) Light as a particle • Although light travels in waves, it also behaves as a particle. • Light particles are called photons. • Photons traveling in short wavelengths have high energy. • Photons traveling in long wavelengths have low energy. • When photons hit atoms, they can excite the atom’s electrons or move them into a higher energy state (Einstein –Photoelectric effect) • These high energy electrons can then form chemical bonds Einstein and the Photoelectric Effect • Albert Einstein won the Nobel Prize for his work on the Photoelectric effect which showed that light can behave as a particle called a photon. • These photons can excite electrons to higher energy levels allowing them to form chemical bonds to make, let’s say, GLUCOSE! Photosynthetic Pigments • A pigment is a substance that absorbs particular wavelengths of light. • The colors that you see are the wavelengths that are reflected, not absorbed. • If chlorophyll is a green pigment, then what wavelength is not being absorbed? • GREEN Photosynthetic Pigments • Chlorophyll: Two kinds – Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B. -Both Chlorophyll A and B absorb red and blue wavelengths and reflect green -Chlorophyll A is the primary photosynthetic pigment – directly involved in converting sun energy into chemical energy -Chlorophyll B and other pigments absorb light energy and transfer the energy to chlorophyll A. Other Photosynthetic Pigments • Carotenes: reflect orange wavelengths • Xanthophylls: reflect yellow wavelengths • These two pigments allow plants to use a wider range of wavelengths than chlorophyll alone. • They are also what gives fall leaves their various colors after the plant shuts down chlorophyll production Absorption Spectrum for Plant Pigments • Absorption spectrum: wavelengths absorbed by a pigment