* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3rd quarter days
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
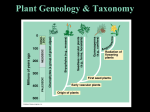
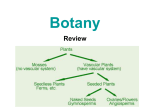
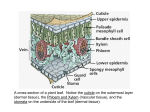
Kingdom Plantae Objective: List the characteristics of plants 1 2 + Kingdom Plantae a. b. Plants are complex multicellular autotrophs; they have specialized cells and tissues. Most plants have vascular tissue, which is made up of specialized cells that play a role in transporting water and dissolved nutrients. Vascular Tissues include: Xylem & Phloem 3 + Kinds of Plants i. Plants without a well-developed system of vascular tissues are called nonvascular plants. Mosses are the most familiar example of nonvascular plants e.g. Liverworts Mosses i. Plants with a well-developed system of vascular tissues are called vascular plants. Their larger, more-complex bodies are organized into roots, stems, and leaves. i. 4 Most plants are vascular plants. + iv. Ferns are the most common and familiar seedless vascular plants. They reproduce with spores that are resistant to drying. iv. Gymnosperms are vascular plants that reproduce using seeds but do not produce flowers. vi. Most plants that produce seeds also produce flowers. Flowering plants are called angiosperms (also include fruit-bearing plants). 5 + Plant Structure + 7 Leaves Photosynthetic organ of the plant, used to convert sunlight into food Stomata: pores within the leaf that open to let CO2 in and O2 out. Guard cells open and close. Cuticle: waxy loss covering on leaf that prevents water + 8 Stems Support plant transport water through xylem transport nutrients through phloem a celery stalk soaked in food coloring will absorb the food coloring, you can see the xylem Two types of stems: herbacious and woody + 9 Roots water and minerals are absorbed (taproots vs fibrous roots) also used to anchor the plant movement of water up to leaves is influenced by TRANSPIRATION + 10 gymnosperms "naked cone seeds” bearing plants (seeds grow on cones) needle like leaves usually stay green year round wind pollinated Examples: pine trees & evergreens + 11 e. Angiosperms flowering seeds plants are enclosed in a fruit most are pollinated by birds & bees have finite growing seasons Examples: grasses, tulips, oaks, dandelions Divided into two main groups: Monocots & Dicots + 12 Monocots vs. Dicots +Angiosperms- 2 types of flowering plants Characterist Description Dicots Monocots Cotyledons Storage tissue that provides nutrition to the developing seedling 2 Cotyledons 1 cotyledon Leaf Venation The pattern of veins in leaves Netted (a branching pattern) Parallel Flowering Parts Number of petals, sepals, stamen and other flowering parts In 4s, 5s, or multiples thereof In 3s or multiples thereof Vascular Bundles Arrangement of bundles of vascular tissue in stems Organized in a circle Scattered ic Fibrous system + 14 Monocots Angiosperms that have 1 seed leaf (cotyledon) parallel veins on leaves 3 part symmetry for flowers fibrous roots Example: lilies, onions, corn, grasses, wheat + 15 Dicots Angiosperms that have 2 seed leaves (cotyledons) net veins on leaves flowers have 4-5 parts taproots Examples: trees and ornamental flowers + + •Reproductive organ of the plant •Flowers are usually both male and female Flower •The male part of the flower is the STAMEN •The female part of the flower is the PISTIL + Plant Reproduction Pollen 18 is produced by the stamen. Pollen moves away from the plant via the wind or other pollinators (birds & bees) The pollen lands on the pistil of another plant and fertilizes the eggs within the ovary The flower petals fall off, the ovary develops into a FRUIT that encloses the seeds Fruits are dispersed in a variety of ways (wind, animals) Fruits are not always edible, anything with a seed inside can be considered a fruit (helicopters, acorns, dandelions) + 19 Asexual Reproduction in Plants Many plants can clone themselves, a process called VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION strawberry plants and other vine like plants send out runners, which grow into new plants some a plant clippings will grow into new plants Potato will grow into a new plant + 20 Perennials - live several years, and reproduce many times, woody plants are perennials Annuals - a plant that completes its life cycle in one growing season (grows, flowers, reproduces and then dies) Biennials - takes two growing seasons to complete, it reproduces in the second growing season