* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint - Colorado FFA
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
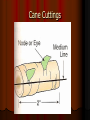
Colorado AgriScience Plant Science Unit 4: Reproduction & Genetics Lesson 4: Asexual Propagation I Asexual Propagation Use of vegetative parts of a plant to increase its number Advantages Economy Time Plants that are identical to the parent Methods Cuttings, culture layering, division, grafting, & tissue Stem Cuttings Tools Sharp knife, single edge razor, & disinfectant Remove all flowers & buds Plant needs to utilize energy for root development Apply Rooting Hormone Use proper soil medium Vegetative Parts of a Plant Stem Tip Cuttings Normally include the terminal bud Stem 2-4” is used Cut made just below the node Remove lower leaves Apply rooting hormone Insert in media deep enough to be self supporting 1 node must be below the surface of the media for root growth to occur Stem Section Cuttings Use middle portion of stem behind the tip cuttings, 2-4” sections are needed Remove lower leaves Cut just above a node on each end Handle as a tip cutting Position the cutting with the right end up Axial buds are always on the tops of the leaves Cane Cuttings For plants with cane like stems Stems cut into sections with 1 or 2 nodes Dust ends with fungicide Dry cane for 1-2 hours Place cane horizontally with half the cane below the surface of the media The eyes or nodes should face upward Cane Cuttings Heel Cuttings Used on woody stemmed plants Shield shaped cut made ½ way through the wood around the leaf & axial bud Apply rooting hormone Insert into media Single-Eye Cuttings Used on plants with alternating leaves Cut ½ “ above & below the node Apply rooting hormone Place vertically or horizontally Double-Eye Cutting Used on plants with opposite leaves Used when stock material is limited Select single node Cut ½” above & below the node Apply rooting hormone Place vertically Leaf Cuttings Made from leaf with the petiole cut to less then ½” Make a clean cut Apply rooting hormone Place vertically in rooting media Leaf Petiole Cuttings Used on a leaf with ½” – 1 ½” long petiole Place vertically in media Several plants will develop from the base of the petiole Leaf Section Cuttings Leaf Section Cuttings Leaves such as begonia are cut into wedges, each containing at least 1 vein Make the cut in a wedge shape with the bottom being the point Done so you can tell the top from the bottom Sections are then placed in media New plants will form where the vein is in contact with the media Split-Vein Cuttings Used with large leaf plants such as begonias Remove leaf from stock plant Slit veins on the bottom surface of the leaf Place the leaf on rooting media with the slits down A new plant will form at each of the slits Split-Vein Cuttings Root Cuttings Use plants that are 2 -3 years old Make cuttings when plant is dormant They will have larger supplies of carbohydrates Top cut is straight & bottom cut is slanted Plants with large roots Use section 4-6 inches long Plants with small roots Use section 1-2 inches long Root Cuttings Store cutting 2-3 weeks in moist peat moss or sand at a temperature of 40 degrees Large roots Plant vertically with the slant cut down Top should be flush with surface of media Small roots Place cutting horizontally ½” below media surface