* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification
Survey
Document related concepts
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
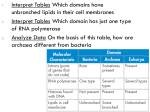
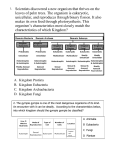
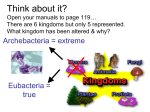
Scientific Classification What’s In a Name?? What are some ways you are classified? gender age social security number income state/area of residence profession Why Classify?? Human nature- we love to put things in their place! Organization Identification Less Confusion Show Relationships Modern Classification Linnaeus Binomial nomenclature Taxon (taxa) phylogenetics- the tracing of evolutionary relationships Haeckel (1894) Three kingdoms Whittaker (1959) Five kingdoms Woese (1977) Six kingdoms Woese (1990) Three domains Eubacteria Bacteria Archaebacteria Archaea Monera Protista Protista Protista Fungi Fungi Plantae Animalia Eukarya Plantae Plantae Animalia Animalia Early history of life Solar system~ 12 billion years ago (bya) Earth~ 4.5 bya Life~ 3.5 to 4.0 bya Prokaryotes~ 3.5 to 2.0 bya stromatolites Oxygen accumulation~ 2.7 bya photosynthetic cyanobacteria Eukaryotic life~ 2.1 bya Muticelluar eukaryotes~ 1.2 bya Animal diversity~ 543 mya Land colonization~ 500 mya Bacteria Kingdom: Monera? Domain: Bacteria Domain: Archaea Prokaryotic- no membrane-bound organelles, microscopic Shape •cocci (sphere) •bacilli (rod) •helical (spiral) Archaea Vs. Eubacteria Domain Archaea no membrane- bound organelles (prok.) no peptidoglycan do not respond to antibiotics extremophiles chemoautotrophs, heterotrophs 3 main groups: methanogens, extreme halophiles, extreme thermophiles Domain Eubacteria no membrane-bound organelles (prok.) peptidoglycan in cell walls growth inhibited by antibiotics diverse metabolism 5 main groups: spirochetes, chlamydias, gram+, cyanobacteria, proteobacteria Prokaryotes Decomposers: unlock organics from corpses and waste products Symbiosis~ •symbiont/host •mutualism (+, + ) •parasitism (+, -) •commensalism (+, 0) Disease •opportunistic: normal residents of host; cause illness when defenses are weakened •Koch’s postulates: criteria for bacterial disease confirmation •exotoxins: bacterial proteins that can produce disease w/o the prokaryote present (botulism) •endotoxins: components of gram - membranes Enter Eukaryotes- Domain Eukarya nucleus membrane-bound organelles larger in size than prokaryotic cells fungus, plant, and animal cells Kingdom Protista (Domain Eukarya) Ingestive (animal-like); protozoa Absorptive (fungus-like) Photosynthetic (plant-like); alga Kingdom Plantae (Domain Eukarya) bryophytes (mosses), pteridophytes (ferns), gymnosperms (pines and conifers); angiosperms (flowering plants) Plants: multicellular, eukaryotic, photosynthetic autotrophs Terrestrial colonization: Vascular tissue The seed The flower Gymnosperms (Kingdom Plantae) Cone-bearing plants Lack enclosed chambers (ovaries) for seeds Ovules and seeds develop on specialized leaves called sporophylls Ginkgo, cycads, and conifers All are “evergreens” Needle-shaped leaves Vascular tissue refinement: tracheids~ water conducting and supportive element of xylem Angiosperms (Kingdom Plantae) Most diverse and geographically widespread of all plants “Flowering plants”(Phy: Anthophyta) Monocots: 1 embryonic seed leaf (lilies, palms, grasses, grain crops) Dicots: 2 embryonic seed leaves (roses, peas, sunflowers, oaks, maples) Vascular tissue refinement: vessel elements/fiber cells Kingdom Fungi (Domain Eukarya) Heterotrophic by absorption (exoenzymes) Decomposers (saprobes), parasites, mutualistic symbionts (lichens) Hyphae: body filaments •septate (cross walls) •coenocytic (no cross walls) Mycelium: network of hyphae Chitin cell walls (polysaccharide) Fungi Diversity, I Phy: Chytridiomycota •aquatic fungi; chytrids •lineage closest to protists (flagella) Phy: Zygomycota •Rhizopus (food mold) •mycorrhizae: mutualistic with plant roots •zygosporangia: resistant structure (freezing and drying) Fungi Diversity, II Phy.: Ascomycota •sac fungi • yeasts, truffles, morels, Sordaria •asci: sexual spores •conidia: asexual spores Phy.: Basidiomycota • club fungus •mushrooms, puffballs, shelf fungus, rusts •basidiocarps: produce sexual spores Kingdom Animalia (Domain Eukarya) heterotrophic most are mobile ingestion followed by digestion multicellular (most have tissues) lack cell walls sexual reproduction 35 phyla- most are marine Animal phylogeny & diversity Monophyletic; colonial flagellated protist ancestor 1- Parazoa-Eumetazoa dichotomy: sponges (Parazoa)~ no true tissues; all other animals (Eumetazoa)~ true tissues 2- Radiata-Bilateria dichotomy: Cnidaria (hydra; ‘jellyfish’; sea anemones) & Ctenophora (comb jellies)~ radial body symmetry; all other animals~ bilateral body symmetry (also: cephalization) Summary 3 Domains- but textbooks are behind: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya 6 kingdom system in most texts: Eubacteria, Archaea, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia classification now based on evolutionary history