* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Methods of Speciation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
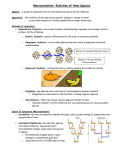
SPECIATION Key Concepts: Isolation and reduced gene flow Biological Species Concept: (Ernst Mayr, 1942) Members of a species successfully interbreed and produce fertile offspring. They are reproductively isolated from other species. Gene flow occurs only between members of the same species. Their reproductive isolation can be in the form of pre-zygotic factors (those things that prevent mating in the first place) or post-zygotic factors (those things that happen after mating) Problems with the BCS: What about asexually reproducing organsims? What about single sex organisms (ex. Killifish) ? What about species that hybridize? Other species concepts; Recognition concept: members of a species recognize each other as potential mates and interbreed. Morphological concept: Members of a species resemble one another and interbreed. Phylogenetic Concept: Members of a species are the smallest set or organisms sharing a common ancestor and DNA lineage. Phenotypic variation matters less than DNA variation. Ecological Concept: Members of a species interbreed and occupy the same ecological niche. Methods of Speciation How New Species May Arise Allopatric Speciation “Different Country Speciation” In this case, members of a population become geographically isolated from each other and thus have very little or no gene flow between them. Mutations arise in the separated population and natural selection happens and over time this population becomes reproductively isolated from the original one. Often thought to be important to populations isolated on islands or by significant geological events. - iguanas blown onto an island by a storm - -squirrels in the Grand Canyon - -fruit fly maltose vs sucrose - -ring species salamanders Sympatric Speciation “Same Country” No geographical barrier is needed in this model Members of the population remain in contact with each other but gene flow becomes reduced between some members of the population How could this happen? Habitat selection (apples vs hawthorns) Polyploidy in plants Sexual selection in fish (cichlids in Lake Malawi)