* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Feeding Relationships
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
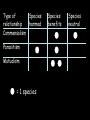
Feeding Relationships Remember Ecology is a study of relationships, including feeding relationships. There are three important terms to know in understanding these relationships: 1. Producer 2. Consumer 3. Decomposer Feeding Relationships Producer- make their own food (autotrophs) They are the basis of every ecosystem and the bottom of every food chain Most are plants! Feeding Relationships Consumer – creatures that ingest food containing the sun’s energy by consuming producers and/or other consumers. Heterotrophs. Four Types: 1. Herbivores 2. Carnivores 3. Omnivores 4. Detrivores Consumers Herbivores: – Eat plants - Are Primary consumers Consumers Carnivores: - eat meat of other consumers - are predators: hunt prey animals for food. Consumers Omnivores - eat both plants and animals (humans are omnivores) Consumers Detrivores: - feed on dead plants and animals. - also called decomposers Decomposers - feed on the dead. - recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem Ex: earthworms, mushrooms Community Interactions 3 Types: 1. Competition: organisms competing for resources 2. Predation: one organism captures and feeds on another (predator/prey) 3. Symbiosis Symbiotic Relationships Symbiosis- two species living closely together 3 Types of symbiosis: 1. Commensalism 2. Mutualism 3. Parasitism Symbiotic Relationships Commensalismone species benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed Ex. orchids on a tree Epiphytes: A plant, such as a tropical orchid or a bromeliad, that grows on another plant upon which it depends for mechanical support but not for nutrients. Also called aerophyte, air plant. Symbiotic Relationships Commensalismone species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped Ex. Egrets following after cattle. Symbiotic Relationships Mutualismrelationship in which both species benefit Ex. Birds cleaning the teeth of a crocodile. Symbiotic Relationships Parasitismone species benefits (parasite) and the other is harmed (host) Ex.: Tick feeding on the blood of a mammal Symbiotic Relationships Parasitism- parasite-host Ex. lampreys, leeches, fleas, ticks,tapeworm Type of Species relationship harmed Commensalism Parasitism Mutualism = 1 species Species benefits Species neutral