* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Ecology
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
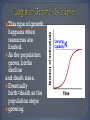
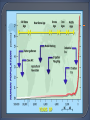
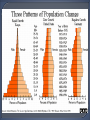
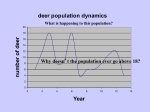
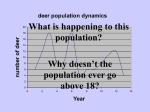
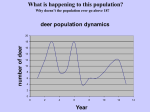
Population- an interbreeding group of individuals of a single species that occupy the same general area. Community-interacting populations that live in the same area. Ecosystem- made of 1 or more communities and the abiotic environment within an area. •Characteristics of Dynamics •Size •Density •Immigration •Emigration •Births •Deaths •Survivorship Anything that restricts the number of individuals in a population. Includes living and nonliving features of the ecosystem density-dependent factors density-independent factors Disease Competition Predators Parasites Food Crowding (space) The greater the population, the greater effect these factors have. (BIOTIC) Volcanic eruptions Temperature Storms Floods Drought Flooding Most are ABIOTIC factors What kind of factor do you think influenced the deaths of these cows? Was it density-dependent or Independent? Explain. Carrying capacity (K): The number of organisms of one species that an environment can support indefinitely. Two of the most basic factors that affect the rate of population growth are the birth rate, and the death rate. This is the maximum population growth under ideal circumstances. Includes plenty of room for each member, unlimited resources (food, water) and no (predators). This type of growth happens when resources are limited. As the population grows, births decline and death rises. Eventually birth=death so the population stops growing. The Exponential curve (also known as a J-curve) occurs when there is no limit to population size. No (K) The Logistic curve (also known as an S-curve) shows the effect of a limiting factor (in this case the carrying capacity (K)of the environment). Humans have learned to expand the carrying capacity of their environment by increasing food supply, combating pests and curing diseases. Can Earth support this increase? Damage to the planet will eventually reduce the carrying capacity for humanity and slow the growth of the human population.