* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome to Class
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
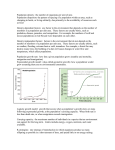
Welcome to Class What does it mean if we have a lot of biodiversity? Agenda • Finish pond study wrap-up • Run-off/pollution readings Welcome to Class What are some water pollutants that come from our homes? Agenda • Populations – Random sampling lab Recall… • Populations – members of a single species that live in once place at a single time Population Characteristics • Population Density – # of organisms per area • Dispersion – pattern of spacing of a population within an area – Based on available resources (food) – 3 typed • Uniform • Clumped • Random Dispersion • Smaller animals usually clump – Larger animals usually independent – Fish Q: What advantage do smaller fish (animals) gain by forming schools (clumped groups)? Safety, confuses predators Q: Which type of population distribution allows you to predict more accurately how many individuals reside in a given area? Welcome to Class What are some things that can limit where a population can live? Agenda • Mark and Recapture lab • Population Notes Agenda • Population Notes Welcome to Class Describe what is happening to the population in the graph below. Population Ranges Limiting Factors • Abiotic conditions – Temperature – Humidity – Rainfall – Sunlight • Biotic conditions – Predators – Competitors – parasites Density independent factors Def. – any factor in an environment that does not depend on the number of members in a population in an area • Abiotic – Weather – drought, flooding, extreme heat/cold, tornados, hurricanes Density Dependent Factors Def. – any factor in the environment that depends on the number of members in a population in an area • Biotic factors – Predation, disease, parasites, competition Predation • More members of a population = more predators Disease/Parasites • Outbreaks of disease tend to occur when population size has increased – Disease in transmitted faster – True for humans as well as animals • Parasites increase at higher densities Competition • When resources become limited animals compete – Within a population or between 2 different species – Lead to starvation – population can decrease Population Growth Rate How to figure out population growth rate • Must know birthrate and mortality • Emigration – moving out of a pop. • Immigration – moving into a pop. – Immigration rate = emigration rate • Calculating growth rate =(population at end – population at beginning) Population at beginning Different Growth Rates Exponential Growth Rate • Starts slow – few organisms • Faster because all organisms are reproducing • Rarely happens – WHY? – Limiting factors – food, space Logistical Growth Rate • Logistic growth occurs when a population’s growth slows or stops following exponential growth – Carrying capacity Carrying Capacity • Maximum number of individuals in a species that an environment can support for the long term – Limited by energy, water, oxygen, nutrients available • Population grows until carrying capacity – Births outnumber deaths – Exceed carrying capacity then deaths outnumber births Reproductive strategies R-strategy (rate strategists) • Produce as many offspring as possible in a short time – Little energy in raising young K-strategists (carrying capacity strategy) • Few offspring that have a better chance of living – Expend a lot of energy raising young Welcome to Class Describe two different strategies of reproduction. Agenda • Quiz • Human Population Growth Human Population Growth Trends in Human Population Growth • Was slow and stable • Recent increase in growth – Technology – agriculture, medicine, shelters • Developing countries add more than developed countries More trends • Zero population growth – birth rate + immigration rate = death rate + emigration rate • Age structure – # of males and females in three age groups • Pre-reproductive (0-19), reproductive (20-44), and post –reproductive (45-80+) Human Carrying Capacity • Humans have a carrying capacity • Technology allows an increase in carrying capacity • Concerns about reaching/exceeding carrying capacity – resources being used