* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. CHAPTER 14 INTRO
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
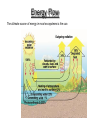
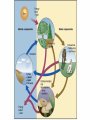
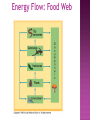
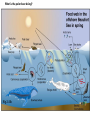
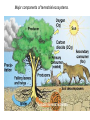
autotrophs Organisms: Energy Sources Producers: plants and bacteria derive energy from inorganic sources phototrophs & chemotrophs heterotrophs Consumers: grazers, carnivores,etc. derive energy from living organisms (organic sources) Decomposers: fungi, scavengers, etc. derive energy from dead organic matter (organic sources) Energy Flow The ultimate source of energy in most ecosystems is the sun. Producer – Photosynthesis – transform radiant energy into chemical energy Ecosystem Structure: how the parts fit together Trophic Structure: major feeding relationships between organisms Producers (Autotrophs) Those members of the community that manufacture organic compounds, such as glucose, from simple inorganic compounds, such as carbon dioxide, using an abiotic energy source, such as sunlight. Through their energy transforming actions, they make chemical energy available as organic compounds for their own use and, directly or indirectly, other members of the living community. Consumers (Heterotrophs) Members of the community that must obtain their energy by eating other organisms or parts of them. All animals are consumers Consumers (Hetertrophs) Consumer animals may be subdivided into the following groups; Herbivores – eat plants Carnivores – eat animals Omnivores – eat both plants and animals Detrivores – eat decomposing organic matter (worms, beetles, crabs) Energy Flow: Food Web TROPHIC LEVELS Radiant energy of sunlight Trees, shrubs, grasses and ferns Producers 1st trophic level Phytoplankton, algae Herbivores Plant-eating insects, small birds, possums Primary Consumers 2nd trophic level Zooplankton, whelks Carnivores Antechinus, owls Secondary Consumers 3rd trophic level Starfish, small fish Snakes, eagles Tertiary Consumers 4th trophic level Large fish, sharks Open forest system Temperate coastal sea ecosystem Categories of Consumers primary consumers: (=herbivores) feed directly on producers; secondary consumers: (=carnivores) feed on primary consumers; tertiary consumers: feed only on carnivores; omnivores: consumers that feed on both plants & animals; scavengers: feed on dead organisms; decomposers (saprobes): consumers that complete the breakdown & recycling of organic materials from the remains & wastes of other organisms; detritivores: feed on detritus (partially decomposed organic matter, such as leaf litter & animal dung). What is the polar bear doing? Fig 2-11b Major components of aquatic ecosystems. Fig. 4–11 Major components of terrestrial ecosystems. Fig. 4–12 The Importance of Decomposers Fig. 4–16 Factors Limiting Populations Law of tolerance: the ability of species to tolerate changes in their environment (physical or chemical factors). Pollution, global warming, habitat loss are some concerns associated with this. Limiting factor: any environmental factor that reduces survival or reproduction within a population. Ex: predation, temperature Limiting factor principle: too much or too little of any abiotic factor can limit or prevent growth of a population, regardless if all other factors are near optimum range of tolerance. Ex: too much fertilizer will kill plants.