* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
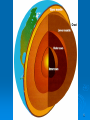
The Biosphere Chapter 3 1 Biotic = living Plants, animals, bacteria, fungus, etc… Abiotic = non-living Rocks, water, air, temperature, sunlight, dirt, etc.. 2 3 3-1 What is Ecology? Ecology = scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment The biosphere contains the combined portions of the planet in which all of life exists, including land, water, and air, or atmosphere. 8 kilometers above Earth's surface to as far as 11 kilometers below the surface of the ocean. 4 5 Levels of Organization Individual = a single organism of a species (a species is a group of organisms so similar to one another that they can breed and produce fertile offspring) Population = groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. Community = groups of different populations that live together in a defined area. 6 An ecosystem is a collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving, or physical, environment. A biome is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities. A biosphere = highest level = all the biomes combined 7 8 3–2 Energy Flow Autotroph (Producer) = organism that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds Photoautotrophs (photosynthesis) • Plants, protists Chemoautotrophs (chemosynthesis) • bacteria 9 10 Consumers Heterotrophs (consumers) = Organisms that rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply Types of consumers: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Detritivores Decomposers 11 12 Feeding Relationships the sun or inorganic compounds autotrophs (producers) various heterotrophs (consumers) from 13 Food Chains a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten 14 15 Food Webs network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem 16 17 18 Trophic Levels step in a food chain or food web 19 Ecological Pyramids a diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web There are 3 different kinds of pyramids: 1.Energy Pyramids 2.Biomass Pyramids 3.Pyramids of Numbers 20 Energy Pyramid Shows the relative amounts of energy available at each trophic level. Organisms store about 10% of this energy; 90% is used up in life processes Much energy is lost as heat. Therefore, usually 4-6 levels in an energy pyramid. 21 22 Biomass Pyramid Represents the amount of living organic matter at each trophic level. grams of organic matter per unit area represents the amount of potential food 23 24 Pyramid of Numbers Shows the relative number of individual organisms at each trophic level. 25 26 Water Cycle 27 28 The Carbon Cycle 29 The Nitrogen Cycle 30 The Phosphorus Cycle 31