* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Down the Rabbit Hole
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Fauna of Africa wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
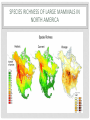
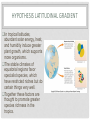
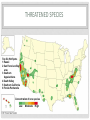
BIODIVERSITY A P E N V I R O N M E N TA L S C I E N C E 3 . 6 B I L L I O N Y E A R S O F E V O L U T I O N O N P L A N E T E A R T H H A S C R E AT E D T H E M I L L I O N S O F S P E C I E S T H AT I N H A B I T T H E E A R T H T O D AY THE ELEMENTS OF BIODIVERSITY Species Diversity: the number or variety of different species in a particular region Species Richness the total number of different species in an ecosystem Species Evenness the extent to which each species is well represented in the ecosystem WORLD WIDE SPECIES RICHNESS • In a study, ecologist Holger Kreft of the University of California, San Diego and his colleagues looked at what they termed “endemism richness”, or the number of unique species combined with the overall number of species around the world. • The researchers were surprised to find that islands from Micronesia to the Atlantic—just 3.6 percent of the surface of the planet—boasted plant endemism richness 9.5 times higher than the continents and more than 8 times higher for vertebrates. SPECIES RICHNESS OF LARGE MAMMALS IN NORTH AMERICA GENETIC DIVERSITY • The variation in DNA composition among individuals within a species. GENETIC DIVERSITY Provides the crucial raw material for adaptation to local conditions. Populations with low genetic diversity are vulnerable to environmental change, disease, and ultimately to extinction. ECOSYSTEM DIVERSITY • Ecosystem diversity refers to variety at levels above the species level, such as ecosystems, communities, habitats, or landscapes. • A coral reef contains far more biodiversity than the same area of an agricultural farm. HOW MANY SPECIES ARE THERE? Good Question – Hard to Know Currently there are about 1.5 million described. The highest estimate is around 100 million. The lowest around 5 million. The best estimate might be around 10 million. It means we've only known about a small fraction of what is presently there. HOW MANY SPECIES ARE THERE? Estimates of biodiversity are incomplete because Difficulty of estimating certain groups microbes, nematodes, fungi, protists, and soildwelling arthropods. Many areas of Earth still remain little explored Deep ocean Tropical rainforest HOW MANY SPECIES ARE THERE? To illustrate: In a famous study conducted in Panama, 19 trees were "fogged" with insecticide and the dead were collected as they fell through the canopy. Nearly 1,200 species of beetles alone were collected. Of those, 80 percent were not known to science. HOW MANY SPECIES ARE THERE? Many of the species that are currently being discovered live in areas that have never before been explored Hydrothermal vents along the floor provide energy for bacteria that use this energy like plants use the energy of the sun. They form the base of a giant food web thousands of feet below the surface. Now scientists believe there could be as many as a million species just in on the ocean floor. UNEVEN SPECIES DISTRIBUTION BUGS RULE THE PLANET! LATITUDINAL GRADIENT Species richness gradually increases as one approaches the equator HYPOTHESIS: LATITUDINAL GRADIENT The variable climates of polar and temperate latitudes favor organisms that can survive a wide range of conditions. Such generalist species have expansive niches; they can do many things well enough to survive, and they spread over large areas. HYPOTHESIS LATITUDINAL GRADIENT In tropical latitudes, abundant solar energy, heat, and humidity induce greater plant growth, which supports more organisms. The stable climates of equatorial regions favor specialist species, which have restricted niches but do certain things very well. Together these factors are thought to promote greater species richness in the tropics. Where Is Declining Biological Diversity the Greatest Problem? THREATENED SPECIES Top Six Hot Spots 1 Hawaii 2 San Francisco Bay area 3 Southern Appalachians 4 Death Valley 5 Southern California 6 Florida Panhandle Concentration of rare species Low Moderate High EXTINCTION OF SPECIES PANDA SAYS: SEE YA LATER – STUDY HARD