* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Competition - University at Buffalo
Survey
Document related concepts
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Holocene extinction wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Extinction debt wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
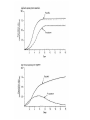
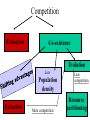
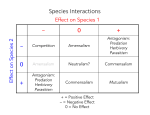
Habitat vs. Niche • Habitat is a place • Niche is a pattern of living – – – – Space utilization Food consumption Temperature range Appropriate mating conditions Competition What is needed for competition to occur? an individual must have the ability to acquire resources and in doing so, makes those resources limited to others Resource competition = A inhibits inhibits B Types of Competition Interference Competition fighting over resources Exploitative Competition consuming shared resources Results of competition 1. One species wins and the other becomes extinct Competitive Exclusion Principle complete competitors cannot co-exist (Gause’s Principle) 2. Co-existence shared habitat a. Shifting advantages e.g. Flour beetles b. Populations are maintain below competitive levels e.g. Influences such as disease and predation Example Results of competition cont c. Resource partitioning: species require different parts of the same resource e.g.. Wood Warblers http://aves.net/photoindex/wood-warblers.html Results of competition cont d. Evolution and Character Displacement e.g. Galapagos Finches Competition Relationships between species species A species B Neutralism =no interactions producing effects on A/B Mutualism A (+) (+) B Competition A (-) (-) B Predation A (+) (-) B Predator prey Mutualism Symbiotic relationships between species Parasitism A (+) Parasite (-) B host Commensalism A (+) B Amensalism A (-) B Commensalism and Amensalism Parasitism Keystone species http://divebums.com/FishID/Page s/giant_spined_star.html http://divebums.com/FishID/Pages/sunflower_star.html Competition Extinction Co-existence Evolution Low Population density Extinction Extinction More competition Less competition Resource partitioning