* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 4: Genetics
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
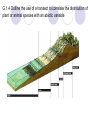
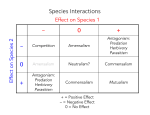
Option G: Ecology and Conservation G.1 Community Ecology What are abiotic factors? Temperature Soil pH Salinity Mineral components Water light Humidity Amount of precipitation Etc. G.1.1 Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species, including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity and mineral nutrients Abiotic factor Explanation Temperature Organisms can only survive within a narrow range from which it is adapted to Light Light intensity/wavelength/duration and quality is important for photosynthesis Soil pH Most plants only tolerate a narrow pH range Salinity Most plants can’t tolerate high fluctuations in salinity Mineral nutrients Affects plant fertility, soil structure, and water retention Water Limiting factor in most terrestrial ecosystems and plants are classified according to their ability to tolerate water shortage G.1.2 Explain the factors that affect the distribution of animal species, including temperature, water, breeding sites, food supply and territory Abiotic/biotic factor Explanation Temperature Must be within viable range of adapted animal Water Must be species-specific quantities Breeding sites Maintenance of species Food supply Right kind for species Territory • Breeding or feeding • Dissolved oxygen affects aquatic species • Salinity may affect some species G.1.3 Describe one method of random sampling based on quadrat methods, that is used to compare the population size of two plant or two animal species The Quadrat Method • Squares of a certain size are made • Randomly choose a square • Organisms within the square are counted • This number is used to determine the population size Why is this method better used for plants rather than animals? Using the quadrat method, find out how many there are of the following: Venus flytraps Roses Orchids Why is this method better used for plants rather than animals? G.1.4 Outline the use of a transect to correlate the distribution of plant or animal species with an abiotic variable G.1.5 Explain what is meant by the niche concept, including an organism’s spatial habitat, its feeding activities and its interactions with other species Spatial habitat: area inhabited by organism Feeding activities: affects ecosystem by keeping other organisms in check Interactions: • Competition • Herbivory • Predation • Parasitism • Mutualism G.1.6 Outline the following interactions between species, giving two examples of each: competition, herbivory, predation, parasitism and mutualism Jigsaw task: You will randomly be placed in expert groups for one type of interaction and you will quickly research and find two examples of it. After you will get back to your home groups and share your findings with them. 1. Competition 2. Herbivory 3. Predation 4. Parasitism 5. Mutualism G.1.7 Explain the principle of competitive exclusion No two species in a community can occupy the same niche G.1.8 Distinguish between fundamental and realized niches* Fundamental niche: • The potential niche of an organism under ideal conditions with its adaptations Realised niche: • The actual niche of an organism which is restricted by the environment and competition G.1.9 Define biomass The total dry organic matter of organisms/ecosystems (g m-2yr-1) G.1.10 Describe one method for measurement of biomass of different trophic levels of the ecosystem • Measure total area of ecosystem (e.g. a forest) • Divide ecosystem into small areas (e.g. grids or plots marked with a stake carrying a number) • Choose one sample plot • Measure size of each plant species (height and diameter). Extract all vegetation from plot. • Dry all samples in circulating drying oven at 90°C • Use mathematical model to show relationship between weight and height of each plant species and its biomass • Sample other plots (size and height only) • For animals, trap them and weight and measure them. Use tables to determine their biomass • Average data for all species per plot • Multiply the average per plot by the number of plots in ecosystem