* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BEVOLKINGSDINAMIKA - Teaching Biology Project
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
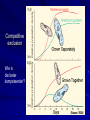
DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION Way to explain changes in population composition e.g. high to low birth rate. FOUR STAGES: STAGE ONE: Both death and birth rate high (preindustrial). Balance in population. DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION STAGE TWO: DEVELOPING COUNTRIES Death rates drop dramatically – better food and sanitation, less disease. Better education, healthcare, access to technology, better farming techniques. Birth rates continue to be high. Increase in population occurs, pressure on economy, health care, education etc. DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION STAGE THREE: DEVELOPING TO DEVELOPED COUNTRIES Birth rates fall – contraception, higher wages, urbanisation, decrease in subsistence agriculture, increase in education and status of women, children don’t work, parents invest in children’s education. DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION STAGE FOUR: DEVELOPED COUNTRIES Low birth rates, low death rates. Birth rate may drop to below replacement level (Germany, Italy, Japan). Death rate may increase due to lifestyle diseases and ageing population. Threat to industries relying on population growth. Economic burden on shrinking working population. Factors that can cause a decrease in population growth Kaposi sarcoma, a skin cancer typical of HIV/AIDS Diseases such as HIV/AIDS, bird flu, H1N1 etc. Better living conditions and better education leading to better family planning. Better contraceptives. Wars. Natural disasters. Factors that influence community structure Predasie Kompetisie Kompeterende uitsluiting Hulpbronafbakening Simbiose Suksessie Predation Competition Competitive exclusion Resource partitioning Symbiosis Succession PREDATOR-PREY-RELATIONSHIP PREDASIE PREDATOR-PREY RELATIONSHIP Direct link between predator and prey numbers. As prey increase, there will be more food for predators, so will predators increase. Increase in predator numbers put pressure on prey numbers. Prey will decrease. Decrease in prey will mean less food for predators, numbers will decrease etc. ROL VAN KOMPETISIE Kompeteer om dieselfde, maar beperkte bronne bv. Water, lig, voedsel, gebied, paarmaat. Intraspesifiek – dieselfde spesie. Interspesifiekverskillende spesies. Hyena and lion Intraspecific or interspecific? Explain your choice Competition 1. Intraspecific competition: the competition between organisms of the same species depending on the same resources like food, space, shelter, water and access to mates. Competition 2. Interspecific competition: the competition between organisms of different species depending on the same resources e.g. light, space, water, shelter, food COMPETITIVE EXCLUSION: The competition in which one of the two competing species is much more successful that the other, to such an extent that the successful species survives and the other species disappears. Kompeterende uitsluiting: Een van die spesies is ‘n baie beter kompeteerder; wanneer hy saam met ‘n ander spesie in diese3lfde habitat is, sal hy oorleef en die ander uitsterf. Competitive exclusion Wie is die beter kompeteerder? RESOURCE PARTITIONING: The kind of competition situation in which competing species coexist in the same habitat since they use the resources slightly differently. HULPBRONAFBAKENING: Kompeterende spesies kan saam bestaan en oorleef omdat hulle bronne op verskillende maniere benut. Resource partitioning amongst plants Resource partitioning: co-existing shore birds Wat is simbiose? Simbiose beteken letterlik “saamleef” – sym = saam, en bio = lewe. Die saamleefverhouding is gewoonlik lewensbelangrik vir ten minste een van die partye. Dit is ‘n langtermyn saamleef en nie toevallig of tydelik nie. MUTUALISME Tot voordeel van beide partye. Geen party word benadeel nie. Voorbeeld: vlinder en blom – blom word bestuif, vlinder kry nektar. Verpligte mutualisme Die saamleefverhouding is lewensbelangrik vir albei partye. Ligene (korsmosse) – swamme verskaf blyplek en absorbeer water; alge fotosinteer en verskaf voedsel. Nie-verpligte mutualisme Die saamleef-verhouding is steeds belangrik,maar nie noodwendig tussen twee spesifieke individue nie bv. Die vlinder en blom (reeds genoem). Die bosluisvoël kry voedsel en die wildsbok is vry van parasiete. KOMMENSALISME Die een party word bevoordeel – die ander party word nie bevoordeel of benadeel nie bv. Beesryer wat hier ‘n saamry-geleentheid kry, maar goggas op grond vreet waar bees vroetel. Nog kommensalisme … Die remora-suigvis gebruik die haai as ‘n taxi en vreet van die afvalstukkies voedsel wanneer die haai vreet. SUIER AAN BO-KANT VAN REMORA PARASITISME Een party word bevoordeel, die ander word beslis benadeel. Parasiete wat op diere teer (en self diere is), kan ektoparasiete of endoparasiete wees. Plantparasiete Semi-parasiete is slegs vir water en minerale van die gasheer afhanklik en kan self fotosinteer bv. voëlent (Viscum). Holoparasiete is geheel en al afhanklik van die gasheer en bevat geen chlorofil nie bv. Dodder. Community change over time: Ecological succession TERMINOLOGY IMPORTANT 1. Primary succession: the sequence of organisms that occupy a new habitat. 2. Pioneer plant: a plant that can colonise bare soil and that is part of the community that forms the first stage in the process of succession 3. Secondary succession: the sequence of organisms that occupy a disturbed habitat or when an established community has been disturbed in a catastrophic manner. 4. Climax community: the final stage in the process of succession that refers to a mature community of plants that will remain stable with few, if any, changes over time The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time Succession PRIMARY SUCCESSION colonization of new sites by communities of organisms – takes place on bare rock PRIMARY SUCCESSION New bare rock comes from 2 sources: PRIMARY SUCCESSION New bare rock comes from 2 sources: PIONEER ORGANISMS the first organisms to colonize a new site Simple plants like mosses and ferns can grow in the new soil plantecology.wordpress.com Wanneer pionierplante bygedra het tot die ontstaan van `n plantgemeenskap, begin diertjies om hulle daar te vestig. Primary SuccessionRock Begins in a place that ALREADY has soil and was once the home of living organisms Occurs faster and has DIFFERENT pioneer species than primary succession. Secondary succession- Secondary succession- CLIMAX COMMUNITY