* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download presentation source
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
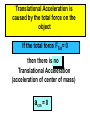
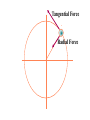
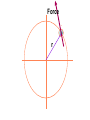
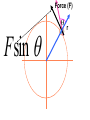
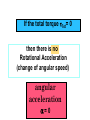
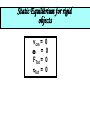
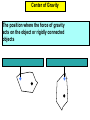
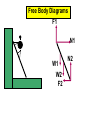
Physics 150/215 Lesson 7 Static Equilibrium • enter of Mass C •Types of Motion •Torque •Types of Equilibrium •Static •Translational - Rotational Conditions for Equilibrium •Center of Gravity •Free Body Diagrams Center of Mass = Average position of the masses For example: 6 kg at x=5m & 7 kg at x=10m x coordinate of center of mass = 6 5 7 10 100 7.69 6 7 13 Think of the average height of 6 monsters that are 5m high and 7 that are 10 m high Motion of an object can be analyzed into three types t•ranslation of the center of mass •rotation (rigid) about the center of mass •vibration (elastic) about center of mass Translational Acceleration is caused by the total force on the object If the total force FTot= 0 then there is no Translational Acceleration (acceleration of center of mass) acm = 0 •Thus vcm = constant I•f velocity of center of mass is initially zero it will stay zero • here may be rotation T or vibrational motion around center of mass Rotational acceleration is caused by the total turning force = TORQUE about the center of mass. Tangential Force Radial Force Force r Force (F) Fsin r Torque Tangential Force radius = FSinr FrSin Fd d rSin Moment / Lever Arm • inear = Translational L •Angular = Rotational Total Force = 0; Total Torque not zero Total Force not 0; Total Torque = 0 If the total torque Tot= 0 then there is no Rotational Acceleration (change of angular speed) angular acceleration = 0 •Thus angular speed = constant I•f angular speed is initially zero •it will stay zero If object is RIGID There will be no vibration about center of mass Static Equilibrium for rigid objects vcm = = FTot = Tot = 0 0 0 0 Conditions for Static Equilibrium for Rigid Objects The center of mass of an object will not accelerate if the total force on the object is zero if Ftot a cm 0 TRANSLATIONAL EQUILIBRIUM An object will have zero angular acceleration if the total torque on the object is zero if 0 ROTATIONAL EQUILIBRIUM If the initial velocity of the center of mass is zero and the initial angular velocity is zero they will remain zero if Ftot and acm 0 When this is so the object is said to be in STATIC EQUILIBRIUM Properties of Torque The torque of a force about any point on the line of action of that force is zero . If a body is in translational equilibrium and the net torque is zero with respect to one point in the body then it is zero with respect to all . points in the body F tot 0 0 = 0 forces Center of Gravity The position where the force of gravity acts on the object or rigidly connected objects Free Body Diagrams F1 N1 W1 W2 F2 N2