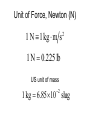* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces and Newton`s Laws
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Forces and Newton’s Laws Forces • Forces are ________ (magnitude and direction) • Contact forces result from ________ ________ • Field forces act ___ __ __________ Fig. 4.2, p. 84 4 Fundamental Forces • • • • Strong nuclear force Electromagnetic force Weak nuclear force Gravitational force • All are ______ forces • Nuclear are _______ ______ (femtometers) • Electromagnetic and gravitational range is _________ Newton’s First Law • An object moves with a constant velocity, unless acted on by a ________ net force. – Velocity is a vector: magnitude and direction • Net force: _______ _____ of all forces exerted on object Inertia vs. Mass • Inertia: tendency of object to continue its _______ in the __________ of forces • Mass: measure of object’s __________ to ________ in _______ due to force Newton’s Second Law • Acceleration of an object is – directly __________ to net force acting on it – _________ proportional to object’s mass F a m F ma 4.1 This is a vector equation Fx max Fy ma y Fz maz 4.2 Unit of Force, Newton (N) 1 N 1 kg m s 2 1 N 0.225 lb US unit of mass 2 1 kg 6.85 10 slug The Gravitational Force • Newton’s Universal Law of gravitation: • Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is: – Directly proportional to the product of the particles’ ___________ – Inversely proportional to the _______ of the __________ between them m1m2 Fg G 2 r Fig. 4.6, p. 90 4.5 Weight • Magnitude of Fg acting on object near Earth’s surface w mg 4.6 • g is acceleration of gravity (of Earth) ME g G 2 r 4.8 • r is radius of Earth (RE) plus height (y) above surface of Earth r RE y Newton’s Third Law • Forces in nature always exist ___ _______ • A _______ __________ force can’t exist • The force F12 exerted by object 1 on object 2 is equal in _________ but opposite in _________ to the force F21 exerted by object 2 on object 1 F12 F21 Fig. 4.7, p. 92 Force Pairs & the Normal Force • TV resting on table attracted by Earth (Fg) • Pair: ______ attracted to ______ (Fg’) • But a = 0, so another force is present. n is _________ force of table on TV • Pair: normal force of _____ on _____ (n’) Fig. 4.8, p. 93 n Fg n is ______________ to contact surface and is _____________ in origin