* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motion and Forces
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
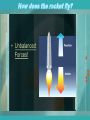
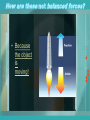
Wednesday November 4, 2015 Unit Question What role do forces play in the world around us? Guiding How do Newton’s Laws affect Question / everyday objects? Learning Target Warm-up Which of Newton’s Laws is responsible for this situation? 1st Law: An object in motion stays in motion Agenda Homework 1. Forces Notes and Diagrams 2. Ramp Demonstration 1. Quiz Friday What is a Force? • Force – push or pull one body exerts on another What is a Force? • Force is measured using the standard metric unit known as the Newton (N). • One Newton is the amount of force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s/s. Thus, the following unit equivalency can be stated: – 1 Newton = 1 kg • m/s2 • A force is a vector quantity. • A vector quantity is a quantity that has both magnitude (size) and direction. • Net force – the combining of forces when two or more forces act on an object • Balanced forces – forces that are equal in size and opposite in direction – Forces are acting on the same object – Do not cause the motion of the object to change • Unbalanced forces – forces that are not equal and/ or opposite in direction – Net force causes object to move in direction of force Unbalanced Balanced How does the rocket fly? • Unbalanced Forces! How are these not balanced forces? • Because the object is moving! Common Forces • Gravity – the attraction two objects have for one another • Air resistance – opposing force an object feels when traveling through air • Friction – resistance to motion caused by two objects in contact with one another. Exit Question • Which way will this block move? Newton’s Labs • Go to your assigned station. • Do not move until instructed to do so. Inertia and Mass • Inertia – the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion – The greater the mass of an object the greater its inertia • Newton’s First Law of Motion – ‘Stuff keeps doin’ what its doin’ until somethin’ else messes with it…’ Check it out… http://www.batesville.k12.in.us/physics/PhyNet/M echanics/Newton1/The_Net_Force.html#NetF orceQuiz F=mxa • Force, mass, and acceleration are all connected. – For any object, the greater the force applied to it, the greater its acceleration will be. Learning Checkpoint • If two equal forces act on an object in opposite directions, what is the acceleration? • According to balanced forces, the acceleration of the object would be zero. Learning Checkpoint • Calculate the force on an object that has a mass of 12 kg and an acceleration of 4 m/s/s. • F = mx a • F = 12 kg x 4 m/s/s • F = 48 kg x m/s/s = 48 N Learning Checkpoint What is the acceleration of a 200 kg object with 3,000 N of net force acting on it? a=F/m a = 3,000 kg x m/s/s / 200 kg a = 15 m/s/s Newton’s Third Law • When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second one exerts a force on the first that is equal in size and opposite in direction. – “To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.” – Example – when you jump on a trampoline the trampoline exerts the same force on you in the opposite direction. Learning Checkpoint • When a force is exerted on a box, an equal and opposite force is exerted by the box. These forces are known as _____ forces. • These forces are actionreaction forces. Learning Checkpoint • What is the difference between weight and mass? • Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is a measure of the force of gravity on the object’s matter.