* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Thermal radiation wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
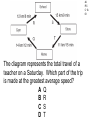
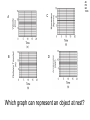
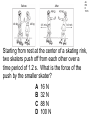
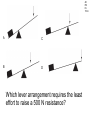
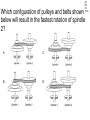
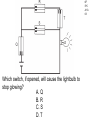
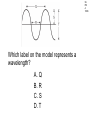
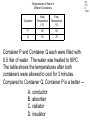
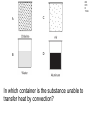
TAKS Physics What do you know? Main Topics • • • • • • • • • • Speed = distance / time Acceleration = velocity change / time Newton’s laws (F = ma) Momentum (p = mv) Energy (conservation) Work and power and simple machines Density = mass / volume Circuits and electricity Waves light and sound Heat transfer Speed = distance / time • You might have to solve for any of these three parts. 4A IPC C 1003 The diagram represents the total travel of a teacher on a Saturday. Which part of the trip is made at the greatest average speed? A Q B R C S D T 4A IPC D 1003 A car traveled 150 km in 2.5 hours. What was its average speed in km per hour? A B C D 37.5 km/h 450 km/h 75 km/h 60 km/h The speed of sound in human tissue is about 1600 m/s. If an ultrasound pulse takes 1.5 x 10-5s to travel through a tissue, what is the thickness of the tissue? A 2.4 km B 2.4 m C 23 cm D 24 mm 4A IPC D 11/05 4A IPC D 11/06 A cyclist moves at a constant speed of 5 m/s. If the cyclist does not accelerate during the next 20 seconds, he will travel --- A B C D 0m 4m 50 m 100m 4A IPC B 10/06 A driver traveled 270 km in 3 hours. The driver’s destination was still 150 km away. What was the driver’s average speed at this point? A B C D 40 km/h 90 km/h 140 km/h 420 km/h 4B IPC GB 10/06 A B C D Which graph can represent an object at rest? Acceleration = velocity change / time • Again, you may have to solve for any of these quantities. • Acceleration is measured in units of meters per second squared 2 •m/s 4A IPC A 11/04 According to this graph, what was the bicycle’s acceleration between 6 and 10 seconds? A B C D 0.0 m/s2 0.65 m/s2 1.6 m/s2 6.5 m/s2 4A IPC C 11/06 The table above shows experimental data collected when four cars moved along a straight-line path. According to these data, which car moved with a constant acceleration of 2 m/s2? A B C D Car Q Car R Car S Car T Newton’s laws (F = ma) • 1st Law - objects resist acceleration • An object at rest tends to remain at rest and an object in motion tends to remain in motion at the same speed and in the same direction unless it is acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s laws (F = ma) • 2nd Law – F = ma • force is equal to mass times acceleration • weight is equal to mass times gravitational acceleration • gravitional acceleration (g) = 9.8 m/s2 Newton’s laws (F = ma) • 3rd Law – for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction • only two forces and only two objects • If object A applies a force on object B, then object B MUST apply the same size force on object A in the opposite direction. 4B IPC D 11/06 A hockey player pushed a puck toward the opposite side of a level ice rink. The player expected the puck to continue all the way across the ice, but the puck slowed and stopped before reaching the other side. Which of these best explains why the puck failed to slide all the way to the opposite side? A B C D The puck’s temperature changed. An upward force acted on the puck. The puck’s momentum remained unchanged. An opposing force acted on the puck. 4B IPC D 11/04 Which factor would most likely cause a communications satellite orbiting Earth to return to Earth from its orbit? A An increase in the satellite’s forward momentum B An increase in solar energy striking the satellite C A decrease in the satellite’s size D A decrease in the satellite’s velocity 4B IPC C The frog leaps from its resting position at the lake’s bank onto a lily pad. If the frog has a mass of 0.5 kg and the acceleration of the leap is 3 m/s2, what is the force the frog exerts on the lake’s bank when leaping? A 0.2 N B 0.8 N C 1.5 N D 6.0 N 4A IPC B 1003 How much force is needed to accelerate a 1,300 kg car at a rate of 1.5 m/s2? A 867 N B 1,950 N C 8,493 N D 16,562 N 4A IPC D 11/05 Starting from rest at the center of a skating rink, two skaters push off from each other over a time period of 1.2 s. What is the force of the push by the smaller skater? A 16 N B 32 N C 88 N D 100 N What is the net force exerted on a 90.0 kg race-car driver while the race car is accelerating from 0 to 44.7 m/s in 4.50 s? A B C D 9.8 N 20 N 201 N 894 N 4A IPC JD 11/06 4B IPC B 490N 11/04 How many newtons of force does a 50.0 kg deer exert on the ground because of gravity? A B C D 49.0N 490N 59.8N 1470N Which of these is the best description of the action-reaction force pair when the space shuttle lifts off from the launchpad? 4B IPC C 11/04 A The ground pushes the rocket up while exhaust gases push down on the ground. B Exhaust gases push down on air while the air pushes up on the rocket. C The rocket pushes exhaust gases down while the exhaust gases push the rocket up. D Gravity pulls the rocket exhaust down while friction pushes up against the atmosphere. 4B IPC D 11/05 The picture above shows the direction in which water leaves the scallop’s shell. Which picture below shows the direction the scallop will move? 4B IPC GB 11/06 When the air is released from a balloon, the air moves in one direction, and the balloon moves in another direction. Which statement does this situation best illustrate? A What goes up must come down. B For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. C The shape and size of an object affect air resistance. D The acceleration due to Earth’s gravity is 9.8 m/s2. 4B IPC D 1004 The illustration above shows a student about to throw a ball while standing on a skateboard. Which illustration below correctly shows the skateboard’s direction of motion after the student releases the ball? Momentum (p = mv) • You may be asked to solve for any of these quantities. • Momentum MUST be conserved. (Along with mass and energy) • The unit is the kilogram meter per second •kg m/s 4A IPC JD 11/05 The table contains data for two wrecking balls being used to demolish a building. What is the difference in momentum between the two wrecking balls? A 300 kgm/s B 200 kgm/s C 150 kgm/s D 0 kgm/s 4A IPC D 11/05 A 0.50 kg ball with a speed of 4.0 m/s strikes a stationary 1.0 kg target. If momentum is conserved, what is the total momentum of the ball and target after the collision? A B C D 0.0 kgm/s 0.5 kgm/s 1.0 kgm/s 2.0 kgm/s 4A IPC HC 11/06 The 500 g cart is moving in a straight line at a constant speed of 2 m/s. Which of the following must to 250 g toy car have in order to maintain the same momentum as the cart? A An acceleration of 5 m/s2 for 2 seconds B A potential energy of 20 J C A constant velocity of 4 m/s D An applied force of 5 N for 5 seconds 4A IPC A 10/04 Which bike rider has the greatest momentum? A B C D A 40 kg person riding at 45 km/h A 50 kg person riding at 35 km/h A 60 kg person riding at 25 km/h A 70 kg person riding at 15 km/h 4A IPC D A ball moving at 30 m/s has a momentum of 15 kg.m/s. The mass of the ball is ___ A B C D 45 kg 15 kg 2.0 kg 0.5 kg Car velocity = 6.3 m/s Driver velocity = 6.3 m/s Driver mass = 100 kg Car velocity = 0 m/s Car velocity = 0 m/s Driver velocity = 6.3 m/s Driver velocity = m/s Driver mass = 100 kg Driver mass = 100 kg 4B IPC 630 11/06 The pictures show how an air bag functions in a collision. How much momentum in kg m/s does the air bag absorb from the crash-test dummy if all the crash-test dummy’s momentum is absorbed by the air bag? Energy (conservation) • Energy must be conserved • Kinetic energy = one half mass times velocity squared • KE = ½ m x v2 • Gravitational potential energy = mass times gravitational acceleration times height • PE = mgh Energy (conservation) • Energy MUST be conserved. • (Along with mass and momentum.) 4A IPC B 11/06 A 1-kilogram ball has a kinetic energy of 50 joules. The velocity of the ball is --- A B C D 5 m/s 10 m/s 25 m/s 50 m/s 6A IPC C What is the potential energy of the rock? A. 59,000 joules B. 64,600 joules C. 93,100 joules D. 121,600 joules 6A IPC B 11/06 What is the approximate difference in gravitational potential energy of the two shaded boxes? A. 19J B. 39J C. 59J D. 79J Solar Radiation and Earth Effect Amount of Energy per Second (terajoules) Solar radiation reaching Earth 173,410 Radiation reflected back into space 52,000 Radiation heating atmosphere, landmasses, and oceans 81,000 Radiation producing winds and ocean currents 370 Radiation used in photosynthesis 40 Radiation resulting in evaporation of water ? 6A IPC A 11/04 Assuming the chart contains all energy transformations in the Earth system, how much solar radiation goes toward evaporating water? A. B. C. D. 40,000 terajoules 92,410 terajoules 121,410 terajoules 133,410 terajoules C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Glucose Water Carbon Water Dioxide 3000 kJ 300 kJ 200 kJ 150 kJ Why is the sum of the product’s energy in this reaction less than the sum of the reactants’ energy? A. Energy is given off as heat. B. The products absorb available energy. C. Energy is trapped in the reactants. D. The reactants’ energy is less than the melting point of glucose. 6A IPC A 11/04 Work and power and simple machines • Work = force times distance • W=Fxd • Power = work divided by time • P=W/t Work and power and simple machines • Work has NO time factor. • If the same force is applied over the same distance, the same work is done even if it is done faster in one case. • If work is done faster, more power is used. Power is how fast work is done. Work and power and simple machines • Two basic types of machines: • Lever type simple machines • (levers, wheel and axles, pulleys) and • Inclined plane type simple machines • (inclined planes, wedges, and screws) Work and power and simple machines • Simple machines may change direction of motion. (Like a pulley) • A machine may also trade distance for force OR trade force for distance. (A machine CANNOT do both.) • A machine CANNOT increase the WORK done. Work and power and simple machines • A simple machine increases output force over a shorter distance by requiring the force you put in to be applied over a longer distance. (You trade distance for force.) Work and power and simple machines • The mechanical advantage of a machine is force output divided by force input. • It is greater than 1 if the machine puts out more force than you put in. • It is less than 1 if the machine puts out less force than you put in. 4A IPC A 1004 How much work is performed when a 50 kg crate is pushed 15 m with a force of 20N? A B C D 300 J 750 J 1,000 J 15,000 J 4A IPC B If a force of 100 newtons was exerted on an object and no work was done, the object must have --A B C D accelerated rapidly remained motionless decreased it velocity gained momentum 4A IPC C 11/04 A mechanic used a hydraulic lift to raise a 12,054 N car 1.89 m above the floor of a garage. It took 4.75 s to raise the car. What was the power output of the lift? A B C D 489 W 1815 W 4796 W 30,294 W 4A IPC C 11/05 A horizontal force of 600 N is used to push a box 8 m across a room. Which of these variables must be known to determine the power used in moving the box? A The weight of the box B The potential energy of the box C The time it takes to move the box D The length of the box A woman lifts a 57-newton weight a distance of 40 centimeters each time she does a particular exercise. It takes her 0.60 second to lift the weight. How much power does she supply for lifting the weight one time? A B C D 24 W 34 W 38 W 95 W 4A IPC c 11/06 An advertisement claims that a certain truck has the most powerful engine in its class. If the engine has more power, which of the following can the truck’s engine do, compared to every other engine in its class? A B C D Produce fewer emissions Operate more efficiently Perform work faster accelerate longer 4A IPC HC 11/06 A person pushes a large box across a level floor by applying a horizontal force of 200 N. If the person pushes the box a distance of 5 meters in 10 seconds, how much work does the person do on the box? A B C D 2000 joules 1000 joules 400 joules 100 joules 4A IPC B 10/06 4A IPC HC 11/04 The weight lifter used a force of 980 N to raise the barbell over her head in 5.21 seconds. Approximately how much work did she do in raising the barbell? A 380 L B 982 J C 2,000 J D 10,000 J 4D IPC FA 11/04 A C B D Which lever arrangement requires the least effort to raise a 500 N resistance? 4D IPC HC 11/06 Which configuration of pulleys and belts shown below will result in the fastest rotation of spindle 2? A C B D 4D IPC C 11/06 Which of these represents a properly balanced system? 4D IPC GB The diagram shows an electric motor lifting a 6 N block a distance of 3 m. The total amount of electrical energy used by the motor is 30 J. How much energy does the motor convert to heat? A B C D 9J 12 J 18 J 21 J Efficiency • Efficiency is calculated by dividing work output by work input and multiplying it by 100%. • The efficiency can NEVER be more than 100%. 4D IPC GB 11/04 What is the efficiency of an air conditioner if there is a work input of 320 J and a work output of 80 J? A B C D 4% 25% 240% 400% Density = mass / volume • Be able to solve for any of the three values. • The unit is grams per milliliter or • grams per cubic centimeter • g/ml or g/cm3 Circuits and electricity • Voltage = current x resistance • V = IR • Power = current x voltage • P = IV 6F IPC A 1004 How much current is flowing through this circuit? A 0.32 A B 3.1 A C 4.0 A D 12.5 A 6F IPC A 10/0 6 In this circuit, how much current flows through the lightbulb? A. 0.75 amp B. 1.50 amps C. 2.0 amps D. 3.0 amps 6F IPC C 10/0 6 The bulb will light when a current supplied by at least one 1.5 V battery is available. Which current will fail to light the bulb? 6F IPC A 1003 Which switch, if opened, will cause the lightbulb to stop glowing? A. Q B. R C. S D. T 6F IPC G 1003 What is the current in a copper wire that has a resistance of 2 ohms and is connected to a 9-volt electrical source? A. B. C. D. 0.22 amp 4.5 amps 11.0 amps 18.0 amps 6F IPC JD 10-04 A C Which circuit is built so that if one lightbulb goes out, the other three lightbulbs will continue to glow? B D Waves light and sound • Velocity = frequency x wavelength • v=fxl • Two types of waves: compression and transverse waves • Sound is a compression (longitudinal) wave • Light is a transverse wave. Properties of Waves • Interference - waves cross over each other • can increase or decrease amplitude Properties of Waves • Resonance - the vibration of one object causes the vibration of another object without contact Properties of Waves • Reflection - a wave ounces off a boundary • The angle of reflection is equal to the angle at which the wave meets the boundary. Properties of Waves • Refraction - the bending of a wave as it changes speed moving from one medium to another Properties of Waves •Diffraction - the bending of a wave as it moves around an obstruction or through an opening Properties of Waves • Polarization - allowing only one orientation of a transverse wave to pass • Only transverse waves can be polarized. 5A IPC B 1004 Which illustration best demonstrates compression waves? 5B IPC C One tuning fork is struck and placed next to an identical fork. The two forks do not touch. The second tuning fork starts to vibrate because of --A. interference B. the Doppler effect C. resonance D. standing waves 5A IPC A 10/06 Which label on the model represents a wavelength? A. Q B. R C. S D. T An empty cup was tightly covered with plastic wrap, and a few grains of salt were sprinkled on top of the plastic. When a tuning fork was struck and placed slightly above the plastic wrap, the salt began to move. Which characteristic of waves does the movement of the salt best demonstrate? A. B. C. D. Echo formation Diffraction Resonance Specular reflection 5B IPC C 11/06 Laser Light Striking a DVD 5B IPC D 11/06 When a DVD is read, laser light touches the DVD surface and is then measured at location A. What allows light to return to location A after striking the DVD surface? A. Conduction B. Refraction C. Magnification D. Reflection 5B IPC A 11/04 The pitch of a sound made by plucking a guitar string is determined by the --- A. frequency of the vibration produced B. strength of the plucking force C. distance between the strings D. shape of the guitar body A tuning fork with a frequency of 256 Hz vibrates when struck. Because of these vibrations, a nearby tuning fork begins to vibrate without being struck. Which of the following best accounts for the vibrations of the second tuning fork? A. Resonance B. Polarization C. Diffraction D. Refraction 5B IPC A 11/05 5B IPC B 11/06 A guitar player is seated next to a piano. The piano player strikes an E key on the piano. The guitarist reports that this causes the E string on his guitar to vibrate. What is the name of this phenomenon? A. Polarization B. Resonance C. Reflection D. Diffraction 5B IPC B 11/04 When trying to spear a fish in water, a person needs to take into account the way light bends as it moves from water into the air. The bending of light as it passes from one medium into another is known as --A. Reflection B. Refraction C. Diffraction D. Polarization 5B IPC F 11/05 A surface wave generated by an earthquake was recorded at Seismic Station 1. Forty seconds later the same wave was recorded at Seismic Station 2. What accounts for the time difference? A.The origin of the wave is closer to Seismic Station 1. B.The speed of the wave decreases with distance. C.The wavelength is longer at Seismic Station 2. D.The wave frequency increases when the wave passes through soil. 5B IPC B 11/04 Which wave has the greatest velocity? 5B IPC D 11/04 Which wave has the least velocity? 5B IPC D 11/06 Diverging lenses are useful to people who suffer from nearsightedness because the lenses can cause images of distant objects to be focused on the retina. Lenses allow images to be focused on the retina because of --A. Diffusion B. Reflection C. Diffraction D. Refraction 5B IPC B 11/05 The diagram shows waves approaching a barrier. Which pattern will be formed after the waves pass through the opening in the barrier? Heat Transfer • Conduction - transfer from one particle to another with contact • Convection - transfer of heat containing particles in a fluid due to differences in density • Radiation - transfer from one particle to another without the need for contact 6B IPC B Heat convection occurs in gases and liquids. Heat convection does not occur in solids because solids are unable to --A. absorb heat by vibrating B. transfer heat by fluid motion C. emit radiation by reflecting light D. exchange heat by direct contact 6B IPC B 11/06 The transfer of heat by the movement of air currents in Earth’s atmosphere is an example of --A. Conduction B. Convection C. Radiation D. Fusion 6B IPC A 10/04 A man who was sleeping wakes up because he hears the smoke alarm go off in his house. Before opening the bedroom door, the man feels the door to see whether it is warm. He is assuming that heat would be transferred through the door by --A. Conduction B. Convection C. Radiation D. Compression 6B IPC C 10/06 In winter the air just above the top bunk of a bunk bed is warmer than the air just above the bottom bunk because warm air rises. Which of the following describes the method of heating that causes this difference in temperature? A. Radiation from the room B. Heat transfer through walls C. Convection currents in the room D. Heat conduction through the bed 6B IPC A 10/06 Which of these is the best example of heat transfer by radiation? A. B. C. D. A satellite is warmed by sunlight. Butter melts on warm bread. A ceiling fan cools a warm room. Puddles of water cool a warm tile floor. 6B IPC D 10/04 Temperatures of Water in Different Containers Container Initial Temperature (oC) Final Temperature (oC) P 90 83 Q 90 76 Container P and Container Q each were filled with 0.5 liter of water. The water was heated to 90oC. The table shows the temperatures after both containers were allowed to cool for 3 minutes. Compared to Container Q, Container P is a better --A. conductor B. absorber C. radiator D. insulator 6B IPC D 11/04 A C B D In which container is the substance unable to transfer heat by convection? 6B IPC J 1003 The primary way liquids and gases transmit heat is by the process of --A. reflection B. convection C. radiation D. convection 6B IPC C A solar heater uses energy from the sun to heat water. The heater’s panel is painted black to --A. Improve emission of infrared radiation B. Reduce the heat loss by convection currents C. Improve absorption of infrared radiation D. Reduce the heater’s conducting properties