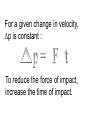* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Momentum
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
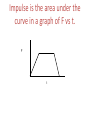
Linear Momentum Physics Mrs. Coyle Linear Momentum, p p= m v • Momentum is a vector. • The direction of momentum is the same as the direction of the velocity of the object. • Unit: kg m/s or N s • “Inertia in Motion” Question 1: • What has more momentum, a dump truck at rest or a pebble moving down a hill at 1m/s? Question 2 • How can you change the momentum of an object? Impulse = Impulse = p = m v = Ft Problem 1 • Starting with Newton’s second law, show that for a constant force, p = m v = Ft . For a given change in velocity, p is constant : To reduce the force of impact, increase the time of impact. Question 3: • How do you have a better chance of winning in a water balloon toss contest? Question 4: • Why does a boxer “roll with the punches”? Question 5: • Why should you follow through in a serve when playing tennis, or when hitting a baseball? Problem 2 A ball at rest has a mass 0.5kg and is kicked with a force of 40N. The impact lasts 0.2s. Find: a) The change in momentum of the ball. b) The final velocity of the ball. Answer: a) 8 Ns, b)16m/s Problem 3 • A football player of mass 130kg travelling at 12.0m/s collides with another player and comes to rest in 0.90s. What was the force of impact? • Answer:1,733N Impulse is the area under the curve in a graph of F vs t. F t Some Engineering Applications Question 6 • Why are airbags used? M A R S E X P L O R A T I O N MARS LANDER AIR BAGS Rover Exits the Lander Applications in Engineering Household Items MILK BOTTLES THE EGG CARTON