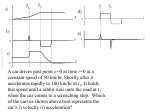
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Net Force
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup