* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces of Motion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
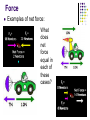
Force Chapter 3 Section 3 Pages 81-86 Force Force – the cause of change in motion, velocity, or acceleration Force is measured in Newtons (N) Any kind of “push” or “pull” Force If you have played billiards, you know that you can force a ball at rest to roll into a pocket by striking it with another ball. The force of the moving ball causes the ball at rest to move in the direction of the force. Force Types of forces 1. Net force – combination / sum of all forces acting on an object 2. Balanced force – net force = 0 Newtons No change in motion Force does not always change velocity. 3. Unbalanced force – net force ≠ 0 Newtons There is a change in motion Force Examples of net force: What does net force equal in each of these cases? Force The net force on the box is zero because the two forces cancel each other. ● Forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction are called balanced forces. Force When two students are pushing with unequal forces in opposite directions, a net force occurs in the direction of the larger force. The net force that moves the box will be the difference between the two forces because they are in opposite directions. This is an unbalanced force. Force The students are pushing on the box in the same direction. These forces are combined, or added together, because they are exerted on the box in the same direction. The net force that acts on this box is found by adding the two forces together. This is also an unbalanced force. Force Everyday forces 1. Friction – force between two objects which opposes motion Depends on the surfaces of the objects Rough surface = more friction (ex. Sandpaper) Smooth surface = less friction (ex. Ice) Force Examples of friction Running on wet grass with or without cleats Force 2. Air resistance – force of air pushing against an object Ex. Wind against a moving car 3. Gravity – force of attraction between two particles of matter due to their mass 4. Normal force – force exerted on one object by another perpendicular to the surface of contact Force Examples of air resistance Force Examples of gravity Force Examples of normal force