* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review PowerPoint
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
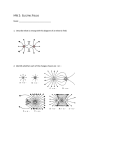
Unit 3 Review An egg is dropped from a third-story window. The distance the egg falls from the window to the ground is closest to (A) 100 mm (B) 102 mm (C) 104 mm (D) 106 mm A runner decreases her speed uniformly from 6.0 m/s to 1.0 m/s over a time of 4 seconds. The magnitude of her acceleration as she travels these 12 meters is (A) 1.9 m/s2 (B) -1.2 m/s2 (C) 1.2 m/s2 (D) 3.8 m/s2 Inertia Which object has the most inertia? (A) a 0.001-kilogram bumblebee traveling at 2 meters per second (B) a 0.1-kilogram baseball traveling at 20 meters per second (C) a 5-kilogram bowling ball traveling at 3 meters per second (D) a 10-kilogram sled at rest A lab cart is loaded with different masses and moved at various velocities. Which diagram shows the cart-mass system with the greatest inertia? A 10-kilogram block is at rest on a plane inclined at 15° to the horizontal. As the angle of the incline is increased to 30°, the mass of the block will (A) decrease (B) increase (C) remain the same Which object has the greatest inertia? (A) a 5.00-kg mass moving at 10.0 m/s (B) a 10.0-kg mass moving at 1.00 m/s (C) a 15.0-kg mass moving at 10.0 m/s (D) a 20.0-kg mass moving at 1.00 m/s A 0.50-kilogram cart is rolling at a speed of 0.40 meter per second. If the speed of the cart is doubled, the inertia of the cart is (A) halved (B) doubled (C) quadrupled (D) unchanged Object Mass (kg) Speed (m/s) A 4 6 B 6 5 C 8 4 D 10 1.5 Which object has the greatest inertia? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D Net Force The vector diagram represents two forces, F1 and F2, simultaneously acting on an object. Which vector best represents the resultant of the two forces? The diagram above represents a 5.0-N force and a 12-N force acting on point P. The resultant of the two forces has a magnitude of (A) 5.0-N (B) 7.0-N (C) 12-N (D) 13-N The diagram above shows a 5.00-kilogram block at rest on a horizontal, frictionless table Which diagram best represents the force exerted on the block by the table? Which diagram represents a box in equilibrium? A 20-N force due north and a 20-N force due east act concurrently on an object. The additional force necessary to bring the object into a state of equilibrium is (A) 20 N, northeast (B) 20 N, southwest (C) 28 N, northeast (D) 28 N, southwest A box is pushed toward the right across a classroom floor. The force of friction on the box is directed toward the (A) left (B) right (C) ceiling (D) floor The diagram represents two concurrent forces. Which vector represents the force that will produce equilibrium with these two forces? A sled and rider slide down a snow-covered hill that makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal. Which vector best represents the direction of the normal force, FN, exerted by the hill on the sled? Which body is in equilibrium? (A) a satellite orbiting Earth in a circular orbit (B) a ball falling freely toward the surface of Earth (C) a car moving with a constant speed along a straight, level road (D) a projectile at the highest point in its trajectory F=ma What is the weight of a 2.00-kilogram object on the surface of Earth? (A) 4.91 N (B) 2.00 N (C) 9.81 N (D) 19.6 N The magnitude of the acceleration of block B is (A) 6.0 m/s2 (B) 2.0 m/s2 (C) 3.0 m/s2 (D) 4.0 m/s2 Two forces, F1 and F2, are applied to a block on a frictionless, horizontal surface. If the magnitude of the block’s acceleration is 2.0 m/s2, what is the mass of the block? (A) 1kg (B) 5kg (C) 6kg (D) 7kg A person weighing 785 Newtons on the surface of Earth would weigh 298 Newtons on the surface of Mars. What is the magnitude of the gravitational field strength on the surface of Mars? (A) 2.63 N/kg (B) 3.72 N/kg (C) 6.09 N/kg (D) 9.81 N/kg A 25-N horizontal force northward and a 35N horizontal force southward act concurrently on a 15-kg object on a frictionless surface. What is the magnitude of the object’s acceleration? (A) 0.67 m/s2 (B) 1.7 m/s2 (C) 2.3 m/s2 (D) 4.0 m/s2 A 60-kg physics student would weigh 1560 N on the surface of planet X. What is the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of planet X? (A) 0.038 m/s2 (B) 6.1 m/s2 (C) 9.8 m/s2 (D) 26 m/s2 rd 3 Law If a 65-kg astronaut exerts a force with a magnitude of 50 N on a satellite that she is repairing, the magnitude of the force that the satellite exerts on her is (A) 0 N (B) 50 N less than her weight (C) 50 N more than her weight (D) 50 N A high school physics student is sitting in a seat reading this question. The magnitude of the force with which the seat is pushing up on the student to support him is closest to (A) 0N (B) 60 N (C) 600N (D) 6,000 N A carpenter hits a nail with a hammer. Compared to the magnitude of the force the hammer exerts on the nail, the magnitude of the force the nail exerts on the hammer during contact is (A) less (B) greater (C) the same A student pulls a 60-Newton sled with a force having a magnitude of 20 Newtons. What is the magnitude of the force that the sled exerts on the student? (A) 20 N (B) 40 N (C) 60 N (D) 80 N Two carts are pushed apart by an expanding spring. If the average force on the 1-kilogram cart is 1 Newton, what is the average force on the 2-kilogram cart? (A) 1 N (B) 0.5 N (C) 0.0 N (D) 4 N A man is pushing a baby stroller. Compared to the magnitude of the force exerted on the stroller by the man, the magnitude of the force exerted on the man by the stroller is (A) zero (B) smaller, but greater than zero (C) larger (D) the same Spring Scale The spring in a scale in the produce department of a supermarket stretches 0.025 meter when a watermelon weighing 1.0 × 102 Newtons is placed on the scale. The spring constant for this spring is (A) 3.2 × 105 N/m (B) 2.5 N/m (C) 4.0 × 103 N/m (D) 3.1 × 10–2 N/m An unstretched spring has a length of 10. centimeters. When the spring is stretched by a force of 16 Newtons, its length is increased to 18 centimeters. What is the spring constant of this spring? (A) 0.89 N/cm (B) 2.0 N/cm (C) 1.6 N/cm (D) 1.8 N/cm A spring hanging vertically that stretches 0.075 meter when a 5.0-Newton block is attached. The value of the spring constant is (A) 38 N/m (B) 67 N/m (C) 130 N/m (D) 650 N/m A person is standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator car. If the scale reads a value greater than the weight of the person at rest, the elevator car could be moving (A) downward at constant speed (B) upward at constant speed (C) downward at increasing speed (D) upward at increasing speed F = ma f = cycles/s Period = = s/cycle = 1/f vc = 2r f = 2r/ Torque = Fr ac = vc2/r F = -G M m r2 Centripetal Which graph best represents the relationship between the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration and the speed of an object moving in a circle of constant radius? The diagram to the right shows an object moves counterclockwise around a horizontal, circular track. Which diagram below represents the direction of both the object’s velocity and the centripetal force acting on the object when it is in the position shown? The diagram represents a mass, m, being swung clockwise at constant speed in a Horizontal circle. If the string were cut at the instant shown, m would hit (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D The diagram represents a mass, m, being swung clockwise at constant speed in a Horizontal circle. At the instant shown, the centripetal force acting on mass m is directed toward point (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D A 1750-kilogram car travels at a constant speed of 15.0 meters per second around a horizontal, circular track with a radius of 45.0 meters. The magnitude of the centripetal force acting on the car is (A) 5.00 N (B) 583 N (C) 8750 N (D) 3.94 × 105 N A student spinning a 0.10-kilogram ball at the end of a 0.50-meter string in a horizontal circle at a constant speed of 10. meters per second. If the magnitude of the force applied to the string by the student's hand is increased, the magnitude of the acceleration of the ball in its circular path will A. decrease B. increase C. remain the same The diagram below shows the elliptical orbit of a comet around the Sun. The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the comet is greatest at point A car moves with a constant speed in a clockwise direction around a circular path of radius r. When the car is in the position shown, its acceleration is directed toward the A. north B. west C. south D. east A car rounds a horizontal curve of constant radius at a constant speed. Which diagram best represents the directions of both the car’s velocity, v, and acceleration, a? A. B. C. D. The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of an object traveling in a horizontal, circular path will decrease if the A. radius of the path is increased B. mass of the object is increased C. direction of motion of the object is reversed D. speed of the object is increased The magnitude of the centripetal force acting on an object traveling in a horizontal, circular path will decrease if the A. radius of the path is increased B. mass of the object is increased C. direction of motion of the object is reversed D. speed of the object is increased In an experiment, a 0.028-kilogram rubber stopper is attached to one end of a string. A student whirls the stopper overhead in a horizontal circle with a radius of 1.0 meter. The stopper completes 15 revolutions in 10. seconds. Find the frequency in revolution/second. In an experiment, a 0.028-kilogram rubber stopper is attached to one end of a string. A student whirls the stopper overhead in a horizontal circle with a radius of 1.0 meter. The stopper completes 15 revolutions in 10. seconds. Find the Period (s). In an experiment, a 0.028-kilogram rubber stopper is attached to one end of a string. A student whirls the stopper overhead in a horizontal circle with a radius of 1.0 meter. The stopper completes 15 revolutions in 10. seconds. Find the tangential velocity in m/s. In an experiment, a 0.028-kilogram rubber stopper is attached to one end of a string. A student whirls the stopper overhead in a horizontal circle with a radius of 1.0 meter. The stopper completes 15 revolutions in 10. seconds. Find the centripetal acceleration in m/s2. In an experiment, a 0.028-kilogram rubber stopper is attached to one end of a string. A student whirls the stopper overhead in a horizontal circle with a radius of 1.0 meter. The stopper completes 15 revolutions in 10. seconds. Find the centripetal force in N. Gravity Which diagram best represents the gravitational forces, Fg, between a satellite, S, and Earth? As a meteor moves from a distance of 16 Earth radii to a distance of 2 Earth radii from the center of Earth, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the meteor and Earth becomes (A) 1/8 as great (B) 4 times as great (C) 8 times as great (D) 64 times as great A satellite weighs 200 N on the surface of Earth. What is its weight at a distance of one Earth radius above the surface of Earth? (A) 50 N (B) 400 N (C) 100 N (D) 800 N A planet is orbiting a star that is about 10 times the size of our sun. If the star were to collapse and become a black hole, what would happen to the gravitational attraction between the star and the planet? A. smaller B. larger C. the same If the Earth were twice as massive as it is now, then the gravitational force between it and the Sun would be A. the same B. twice as great C. half as great D. four times as great Compared to the mass of an object at the surface of the Earth, the mass of the object a distance of two Earth radii from the center of the Earth is A. the same B. twice as great C. one-half as great D. one-fourth as great Two objects of equal mass are a fixed distance apart. If the mass of each object could be tripled, the gravitational force between the objects would A. decrease by one-third B. triple C. decrease by one-ninth D. increase 9 times Which graph represents the relationship between the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by Earth on a spacecraft and the distance between the center of the spacecraft and center of Earth? A. B. C. D. What is the period of orbit of a communications satellite in geosynchronous orbit about Earth? A. 1 year B. 24 hours C. 12 hours D. 60 minutes An artificial satellite makes 4 complete revolutions about the Earth in 8 hours. The period of revolution of the satellite is A. ½ hour B. 2 hours C. 8 hours D. 32 hours In order to experience weightlessness in a spaceship, an astronaut must have an acceleration that is A. less than that of the ship B. more than that of the ship C. the same as that of the ship Which satellite has the greatest tangential velocity (m/s)? A. A B. B C. C D. D Which satellite has the longest period? A. A B. B C. C D. D The radius of Mars is approximately onehalf the radius of Earth, and the mass of Mars is approximately one-tenth the mass of Earth. Compared to the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth, the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars is A. smaller B. larger C. the same