* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces and Motion Review2
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Rolling resistance wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
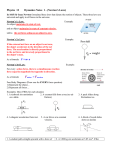
Forces and Motion Review 8th Grade TAG Physical Science Force Define Force: A push or pull What are the Units of force? N (newton) How do forces affect the motion of an object? When forces are balanced, what is the net force? Net force is = 0 If the net force is 0, how does this relate to acceleration? No acceleration When forces are balanced, what does this mean for the objects motion? no change in an objects motion. How do forces affect the motion of an object? When an unbalanced force acts on an object, is there a net force? Yes. Net force > 0 When there is an unbalanced force is there acceleration? Yes…the object accelerates. Can on object be moving and still accelerate? Yes! Ex: Driving on GA400 at a constant velocity (56 mi/hr), not speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction. Car is moving, but 0 acceleration, Fnet=0 Friction A force resulting from 2 objects moving past each other What are the 3 types: Sliding, Rolling, Fluid Friction What is friction dependent on? (hint: think of the lab experiment…if you finished) We increased the mass and the resulting force was increased We changed the surface (table, carpet, sandpaper,duct tape) and the force changed Coefficient of friction, 0 to 1 If close to 0, very low friction If close to 1, high friction Friction (cont.) Friction acts in a direction opposite to motion Force of Friction=Ffr Speed vs. Velocity-very similar! Speed How fast something is going Units of mi/hr or m/s Ex: driving on GA400 at a speed of 65mi/hr Can NOT draw a vector for speed Velocity The speed of an object in a particular direction Units of mi/hr north or m/s north Ex: driving on GA400 at a velocity of 65mi/hr north (included direction) Can draw a vector for velocity (since vector shows magnitude and direction) Acceleration The rate at which velocity changes over time Units of m/s2 If an object is speeding up, slowing down, turning…there is acceleration Net force diagram of toy car (fnet): Fnet Being pushed across floor Fnet Hand let go, and still rolling across the floor Is car speeding up, slowing down, no change? Is car speeding up, slowing down, no change? Speeding up (so accelerating) Slowing down, so accelerating (negative or deceleration) Car stopped What is the Net Force? Fnet = 0 Is car speeding up, slowing down, no change? No change, so no acceleration Acceleration (cont) All objects accelerate toward the earth at the same rate, regardless of their mass All objects accelerate toward Earth at a rate of 9.8 m/s2 Air resistance (fluid friction) affects some objects more than others (depends on size and shape of object) Fair Fair Fg Fg The force of gravity is the same for both pieces of paper Falling Objects What happens to the air resistance as the speed of a falling object increases? Air resistance increases Fair Fair Fg Fg Falling Objects (cont) What happens when air resistance of a falling object becomes equal to the downward force of gravity? Fg = Fair, so Fnet =0 (object stops Fair accelerating…but still moving) The object is falling at a constant velocity TERMINAL VELOCITY Fg Ex: Toy Car Drag toy car across the floor at a constant speed Fn Direction of Motion Force of the pull continues to act on the car (hand still touching car) Which direction is friction acting? Opposite to motion of car Is object moving? Fpull Yes Ffr Fg What is Fnet? Fnet = 0 Is there acceleration? No (since no change in motion) Ex: Toy Car after it just comes off a ramp. Direction of motion Fn Are the forces Balanced or Unbalanced? Note: Fn & Fg equal in length but opposite direction Ffr Fg Force Diagram Unbalanced Fnet Is the car speeding up, slowing down or speed not changing? Slowing Down, so still has acceleration. Ex: Soccer Ball, rolling on the ground, just after the kick Direction of motion Remember, there is nothing pushing the ball forward after the kick, so no more forward force. Is there an Fnet? Fn Yes! How is the ball’s motion changing? Ffr Slowing down Fnet Fg So..is there acceleration? Yes! (negative acceleration)